Tan2 Identity

Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab

Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 6 Trigonometric Identities Exercise 6 1 Get Pdf

Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia

Page 48 Higher Algebra
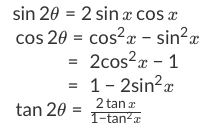
How To Use Double Angle Identities Studypug

Double And Half Angle Formulas
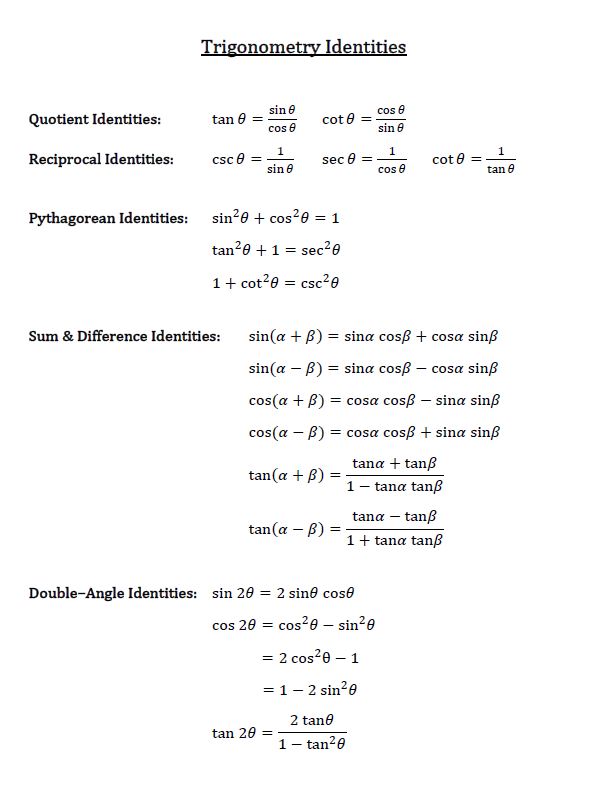
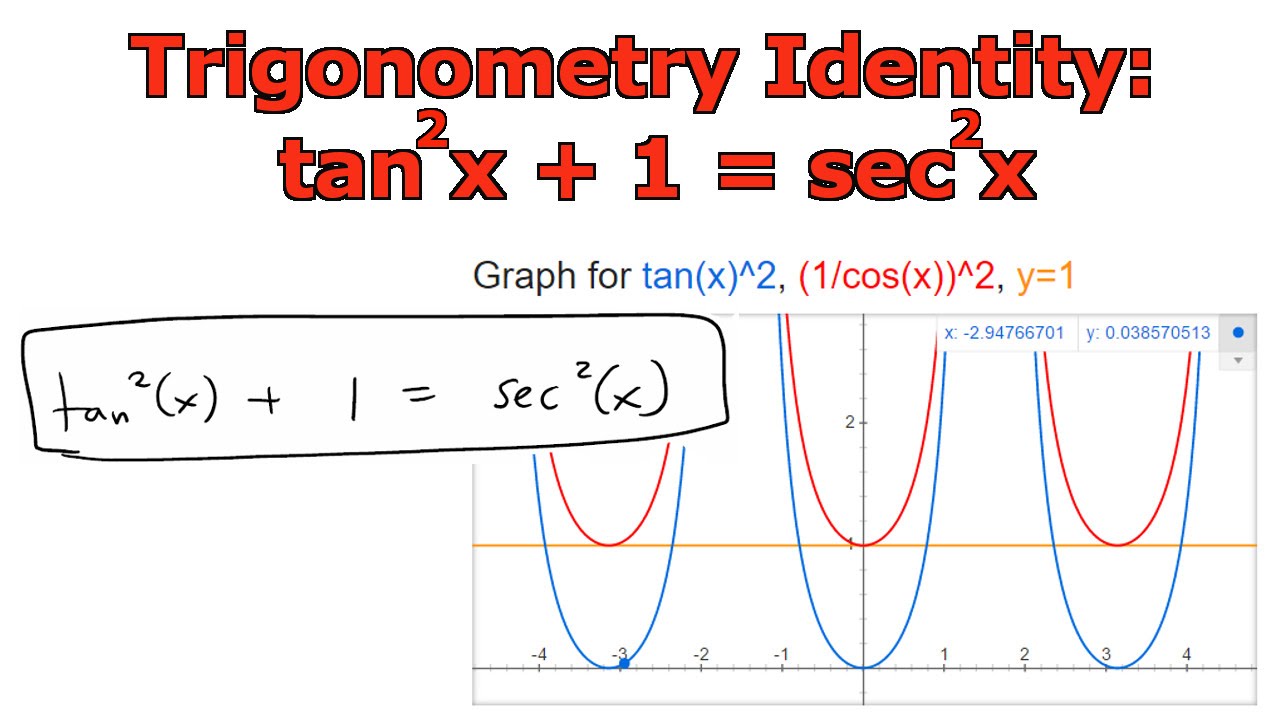
Tan ^2 (x) + 1 = sec ^2 (x) cot ^2 (x) + 1 = csc ^2 (x) sin(x y) = sin x cos y cos x sin y cos(x y) = cos x cosy sin x sin y.
Tan2 identity. $\sec^2{x}-\tan^2{x} \,=\, 1$ $\sec^2{A}-\tan^2{A} \,=\, 1$ Remember, the angle of a right triangle can be represented by any symbol but the relationship between secant and tan functions must be written in that symbol. What does it mean to prove a trigonometric identity?. Trigonometric Identities and Formulas.
Write in sines and cosines using the quotient identity. X and y are independent variables, ;. Divide both sides by cos 2 (θ) to get the identity 1 + tan 2 (θ) = sec 2 (θ).
In the second method, we split the fraction, putting both terms in the numerator over the common denominator. I am horribly stuck with a calc question. As it is known that tan a is not defined for a = 90° therefore identity 2 obtained above is true for 0 ≤ A <90.
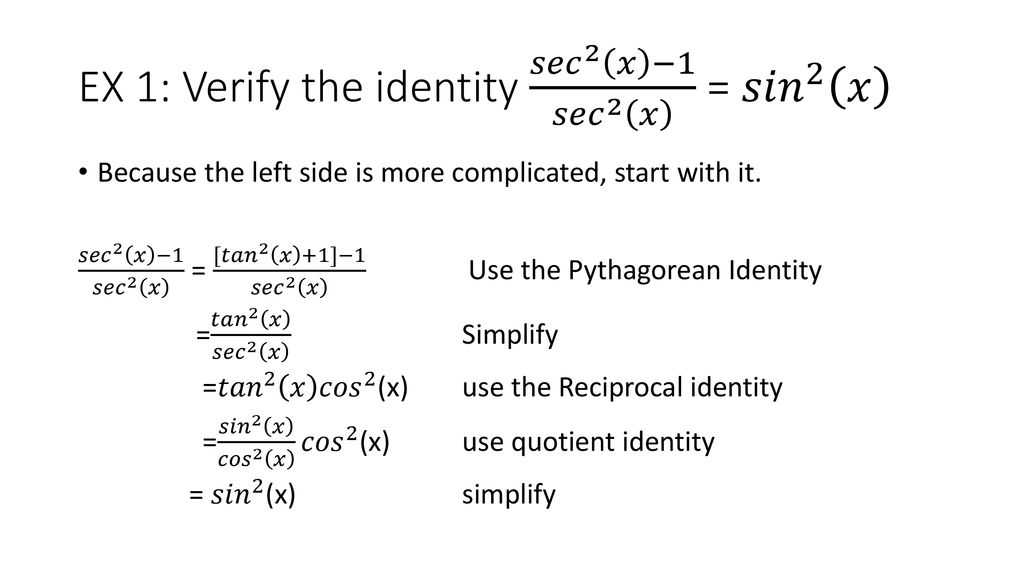
Sec^2 x = sec^2 x. 2 tan(x) sin(2x) 1 + tan2x) Write the more complicated side of the equation in terms of sin(x) and cos(x). $\tan^2{\theta} \,=\, \sec^2{\theta}-1$ The square of tan function equals to the subtraction of one from the square of secant function is called the tan squared formula.
This problem illustrates that there are multiple ways we can verify an identity. Tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ - 1 sec 2 θ = tan 2 θ + 1 sec 2 θ - tan 2 θ = 1 Trigonometric Identity Problems. Prove that tan 60 = (2 tan 30) / (1-tan^2 30) Determine whether the statement is true or not.
How do you simplify #(1-tan^2(x)) /( 1+tan^2(x))#?. High School Math Solutions – Trigonometry Calculator, Trig Identities. When you write out the proof of an identity, you should transform the expression on one side of the identity into the expression on the other side, showing one step of the calculation on each line of your proof.
Tan 2 x - sec 2 x = 1. These three categories of trig identities are used less often. If the angles of the triangle are in arithmetic progression, then what is the length of the third side in.
In the second method, we split the fraction, putting both terms in the numerator over the common denominator. Tan 2 θ +(2 – √6) tan θ – √2 = 0 :. 1 Answer Tiago Hands Apr 15, 15 Answer link.
Tan x = sin x/cos x:. Like sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1 and 1 + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ etc. To prove the 2nd Pythagorean Identity, we start with the 1st.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. The tangent functions are often involved in trigonometric expressions and equations in square form. Trig identities are very similar to this concept.
Federal judge's son killed, husband shot at N.J. Introduction to Tan double angle formula. D is the differential operator, int is the integration operator, C is the constant of integration.
= sec x cot x cot x Rule?. Tan(2 x) = Double-Angle Identity:. Rearranging, you absolutely get:.
The Elementary Identities Let (x;y) be the point on the unit circle centered at (0;0) that determines the angletrad:. Derive Double Angle Formulae for Tan 2 Theta \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1-tan^{2}x} \) let’s recall the addition formula. Then divide every term by \(\cos^2(x)\) and simplify.
Verify the identity. 'Okay, we're leaving now':. Cot 2 (x) + 1 = csc 2 (x).
This is because the actual term used does not matter. Tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ − 1 cot 2 θ + 1 = csc 2. In the first method, we used the identity latex{\sec }^{2}\theta ={\tan }^{2}\theta +1\\/latex and continued to simplify.
These identities can be useful in calculus for converting rational functions in sine and cosine to functions of t in order to find their antiderivatives. Start with the original equation to prove:. Related Symbolab blog posts.
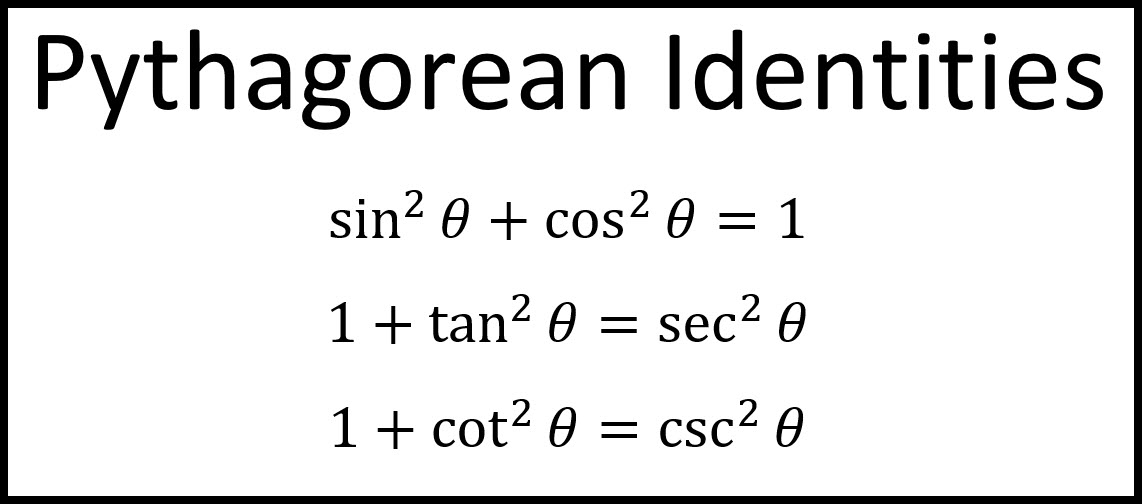
Dividing the equation (1) by BC 2, we get \(\frac{AC^2}{BC^2}\) = \(\frac{AB^2}{BC^2}~ +~\frac{BC^2}{BC^2}\) \(⇒\frac{AC^2}{BC^2}\) = \(\frac{AB^2}{BC^2}+1\). Good luck and be sure to memorize the three Pythagorean identities!. Other Forms of Pythagorean Identity From the Pythagorean Identity, we have the following corollaries:.
Replace tan with sin/cos (sin 2 x/cos 2 x) - sin 2 x = (sin 2 x/cos 2 x)(sin 2 x). Sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2 while tangent and cotangent have period. In a triangle, the length of the two larger sides are 12 cm and 7 cm, respectively.
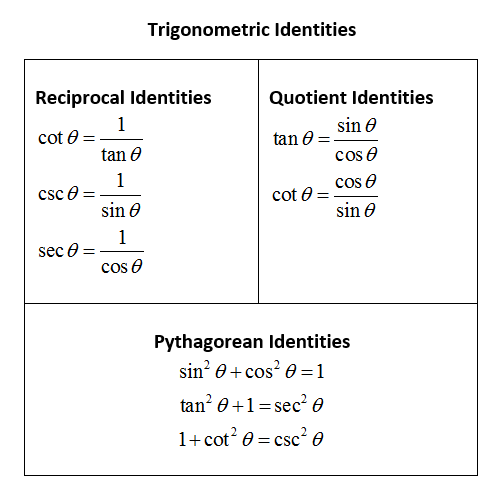
In mathematics, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables where both sides of the equality are defined. We have certain trigonometric identities. Trigonometric identities a sin 2 cos 2 1 b tan 2 1 sec 2 c cot 2 1 cosec 2 from MB 104 at UCSI University, Cheras.
In the first method, we used the identity \({\sec}^2 \theta={\tan}^2 \theta+1\) and continued to simplify. Note, I have used different terms to indicate the angles. 2 cOS x 2 COS x Rule ?.
Sin 2 (x) + cos 2 (x) = 1. Below are some of the most important definitions, identities and formulas in trigonometry. Identities and equations compared:.
1+tan2θ =sec2θ 1 + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ. Identities expressing trig functions in terms of their complements cos t = sin(/2 – t) sin t = cos(/2 – t) cot t = tan(/2 – t) tan t = cot(/2 – t) csc t = sec(/2 – t) sec t = csc(/2 – t) Periodicity of trig functions. Add fractions (cos^2 x+ sin^2 x)/cos^2 x = sec^2 x.
Adjacent is always next to the angle. Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles sin X = opp / hyp = a / c , csc X = hyp / opp = c / a tan X = opp / adj = a / b , cot X = adj / opp = b / a cos X = adj / hyp = b / c , sec X = hyp / adj = c / b ,. Tap for more steps.
These are as follows:. 1/cos^2 x = sec^2 x. The double-angle identity is a modified form of the sum of angle formula in which both the angles are the same.
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge. Recall that the de nitions of the trigonometric functions for this angle are sint = y tant = y x sect = 1 y cost = x cott = x y csct = 1 x:. Some of the most commonly used trigonometric identities are derived from the Pythagorean Theorem, like the following:.
Tap for more steps. In the second method, we split the fraction, putting both terms in the numerator over the common denominator. Sin2θ+cos2θ = 1 sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1.
Csc x = 1/sin x:. The Trigonometric Identities are equations that are true for Right Angled Triangles. Precalculus (2nd Edition) Edit edition.
Tan 2 (x) + 1 = sec 2 (x). (If it is not a Right Angled Triangle go to the Triangle Identities page.) Each side of a right triangle has a name:. Learn how to prove the Pythagorean identity of secant and tan functions in mathematical form by geometrical method.
Sin 2 (x) + cos 2 (x) = 1 1 + tan 2 (x) = sec 2 (x). 1 + tan 2 θ) = sec 2 (θ). Cos(2a) = 1 - tan?(Q) 1 + tan(a) Prove the identity.
These de nitions readily establish the rst of the elementary or fundamental identities given in the table below. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles.They are distinct from triangle identities, which are identities potentially involving angles but also involving. 1- 1 - tan2@) 1 + tan2(a) sin.
2 cos(x) 2 tan(x) 1 + tan2(x) 1 + cos2x) cos2(x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x) 1 + sin?(x) cos(x) 2 II cos2(x) + sin2(x) 2 sin(x) cos(x) 11 = Consider the following. In this video you are shown how the double angle identities are derived from the addition (sum and difference) identities Trigonometric Double Angle Identities | ExamSolutions - youtube Video Stuart the ExamSolutions Guy T22:27:55+00:00. 1+tan^2 (x) = sec^2 (x) write tan in terms of sin/cos and set common denominator.
An identity is a statement that is always true, whereas an equation is only true under certain conditions. This problem illustrates that there are multiple ways we can verify an identity. Verify the Identity 1/(tan(x)+cot(x))=sin(x)cos(x) Start on the left side.
Kanye campaign stop baffles. Problem 62E from Chapter 5.2:. In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true.
Cos(x y) = cos x cosy sin x sin y. Let us see them with this identity:. All of the following are trigonometric identities.
Convert to sines and cosines. In the first method, we used the identity sec 2 θ = tan 2 θ + 1 sec 2 θ = tan 2 θ + 1 and continued to simplify. Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities and Equations Proving Identities.
These are inversions of the double-angle identities. You should look through them to make sure you understand them, but they typically don’t need to be memorized. Let’s look at trigonometric formulae also called as the double angle formulae having double angles.
Divide both sides by sin 2 (θ) to get the identity 1 + cot 2 (θ) = csc 2 (θ). $$sin2(θ) = {1/2}(1-cos (2θ))$$. For example 3x + 2x = 5x is an identity that is always true, no matter what the value of x, whereas 3x = 15 is.
Calculate general solution of the equation:. Thus, \(1 + \tan^2 t = \dfrac{1}{\cos^2 t}\text{,}\) and the identity is proved. Trigonometric identities are equations involving the trigonometric functions that are true for every value of the variables involved.
Obtain a common denominator on left, simplify right (sin 2 x - sin 2 x cos 2 x. It is also called as the square of tan function identity. Sin(x y) = sin x cos y cos x sin y.
In a previous post, we talked about trig simplification. Cot x = cos x/sin x:. When trying to prove trig identities, it is often helpful to convert TAN functions into SIN/COS functions:.
Rearranging, you absolutely get:. 2nd Pythagorean Identity $$\tan^2(x) + 1 = \sec^2(x)$$ Proving the 2nd Pythagorean Identity. Such identities are identities in the sense that they hold for all value of the angles which satisfy the given condition among them and they are called conditional identities.
In the first form, the sign is determined by the quadrant in which the angle α/2 is located. Sec x = 1/cos x:. Write in sines and cosines using the quotient identity.
Allegedly drunk driver kills 3 riders, injures 9 others. Cos^2 x/cos^2 x + sin^2 x/cos^2 x = sec^2 x. These can be "trivially" true, like "x = x" or usefully true, such as the Pythagorean Theorem's "a 2 + b 2 = c 2" for right triangles.There are loads of trigonometric identities, but the following are the ones you're most likely to see and use.
If tan 2 θ = m n, \tan^2\theta=\frac { m }{ n }, tan 2 θ = n m , where m m m and n n n are coprime positive integers, find m n. Rule Statement ( 'x)cot's 1 tan 2 2 Rule?. Verify the identity tan (α/2) = (1 − cos α)/sin α.
Verify the identity tan (α − 2) = sin π/(1 + cos α). Explain how the identities $1+\tan ^{2} \theta=\sec ^{2} \theta$ and $\cot ^{2} \theta+1=\csc ^{2} \theta$ can be derived from the identity $\cos ^{2} \theta+\sin ^{2} \theta=1$ b. I have to write a proof that => tan^2 (theta) - sin^2 (theta) = tan^2 (theta) sin^2 (theta) (where LHS = RHS) Thanks in advance for any help what so ever.
There are three improtant trigonometric identities which are extensively used throughout the topic of trigonometry. Feel free to verify / prove using the identities described in the tutorial:. Trigonometry Q&A Library TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONS Verifying a trigonometric identity Complete the proof of the identity by choosing the Rule that justifies each step (1 +tan2x)cot2x=csc2x To see a detailed description of a Rule, select the More Information Button to the right of the Rule.
This problem illustrates that there are multiple ways we can verify an identity. The half‐angle identity for tangent can be written in three different forms. Use sin^2 + cos ^2 identity.
1+tan 2 a = sec 2 a. Employing some creativity can. Technically, the existence of the tangent half-angle formulae stems from the fact that the circle is an algebraic curve of genus 0.
The identity $\cos ^{2} \theta+\sin ^{2} \theta=1$ is true for all real numbers. The identity, as you noted, is tan 2 x + 1 = sec 2 x, for all values of x. $$tan(2θ)={2 tan(θ)}/{1– tan^2(θ)}$$ Additional Trig Identities.
Simplify the complex fraction. 1 +cot2θ = cosec2θ 1 + cot 2 θ = c o sec 2 θ. Prove that tan 3x tan 2 tan = tan 3x – tan 2 – tan :.

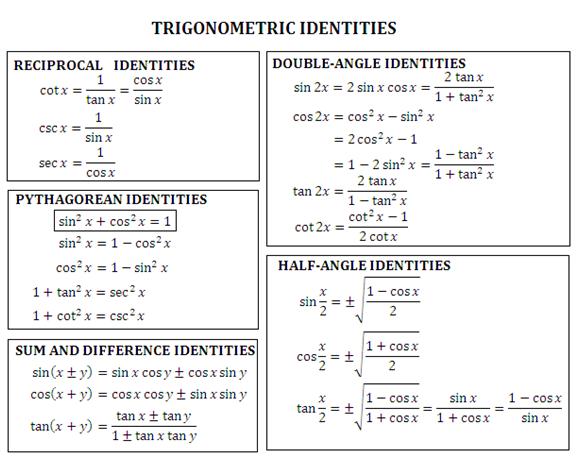
14 2 Trigonometric Identities

Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
2
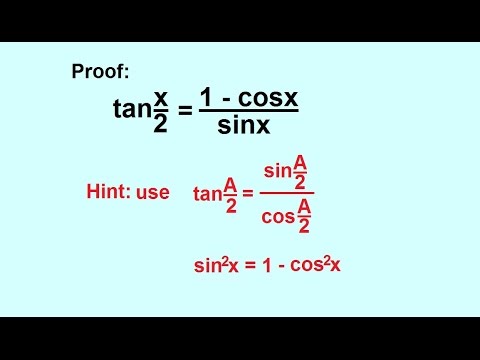
Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 34 Of 57 Proof Half Angle Formula Tan X 2 Youtube
2
2
Http Www Anderson1 K12 Sc Us Cms Lib04 Sc Centricity Domain 1150 S15 hpc trig review keys Pdf

Algebra 39 104 Sec Tan 2 1 Sin 1 Sin 104 Answer Sec Tan 2 Sec 2 2sectan Tan2 1 2sin Sin2 2 Cos2 Cos Cos2 1 2sin Sin2 1 Sin 2 1 Sin 2 1 Sin Course Hero
What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora

Half Angle And Double Angle Formulas Wyzant Resources
How To Use Double Angle Identities Studypug
Trigonometry Pythagorean Identities Andymath Com
2
2

Trigonometry Problems And Questions With Solutions Grade 12 Pages 1 6 Text Version Fliphtml5

Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia

Prove That Sin8 Cos8 1 Sin8 Cos8 1 1 Sec8 Tan8 Using The Identity Sec2 1 Tan28
Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions
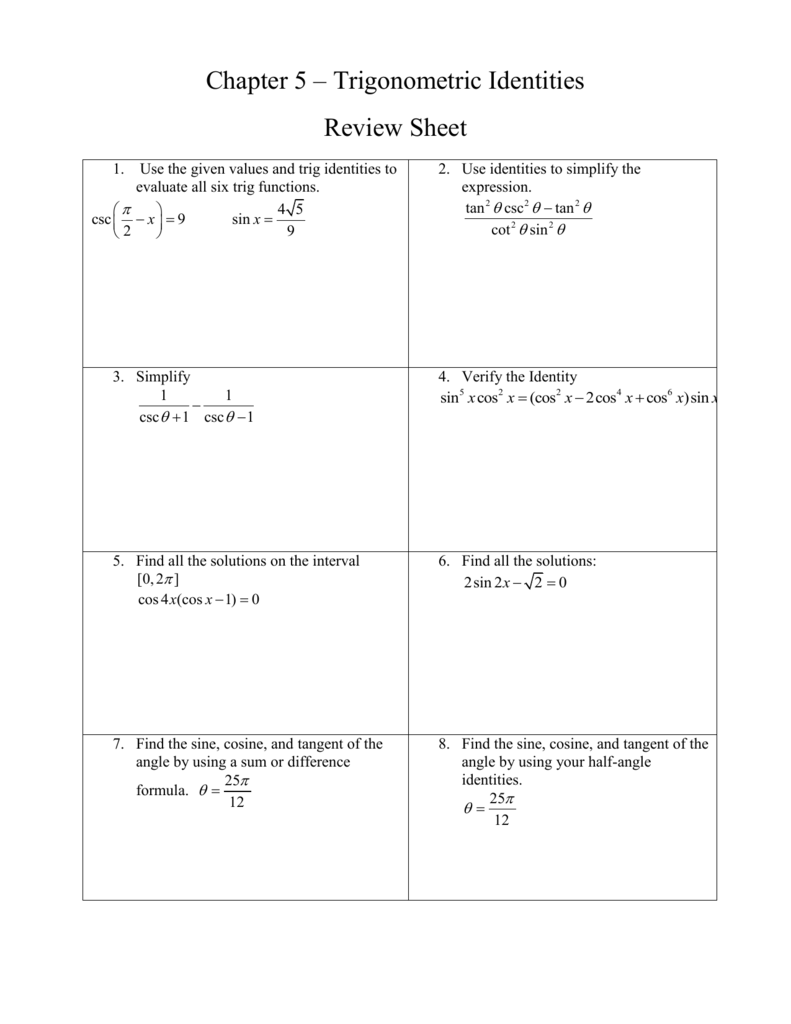
Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities Review Sheet

How Is Secx Tanx Tan P 4 X 2 Quora

How To Solve Independent Trig Identities No Clue How To Solve Or Set Up And Trying To Meet Deadline Askmath
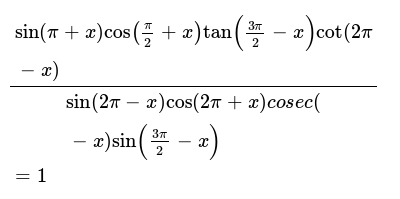
Which Of The Following In An Identity A Sin 2 X Sec 2 X 1 Tan

Solved 2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove Chegg Com
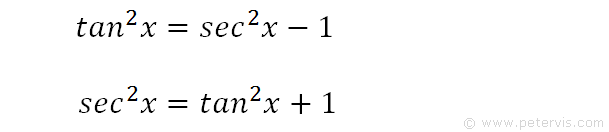
Integrate Sec 2x Method 1
Trigonometric Identities Topics In Trigonometry
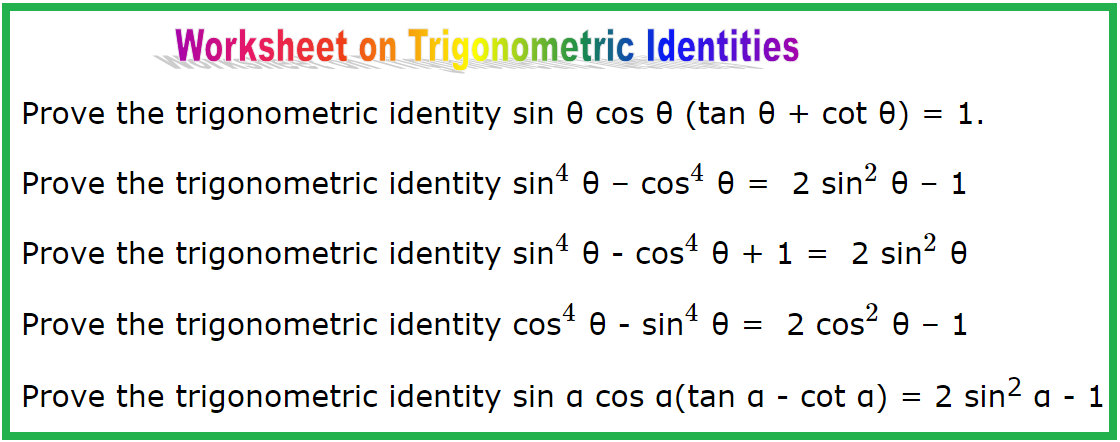
Worksheet On Trigonometric Identities Establishing Identities Hints
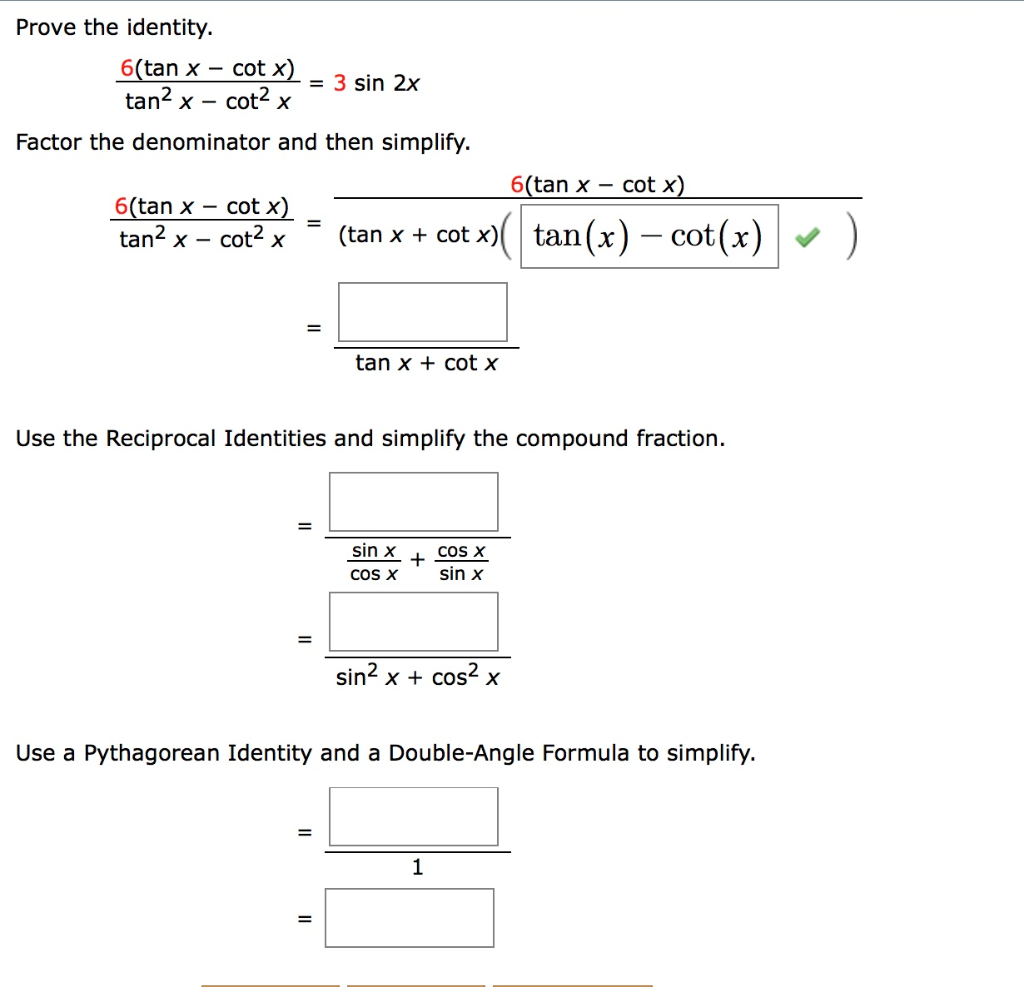
Solved Prove The Identity 6 Tan X Cot X Tan2 X Cot2 Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrvqj 5tvguqi Cb6mlxtmazuxjc23isvenlolikcbmbui6ysck Usqp Cau

14 2 Trigonometric Identities
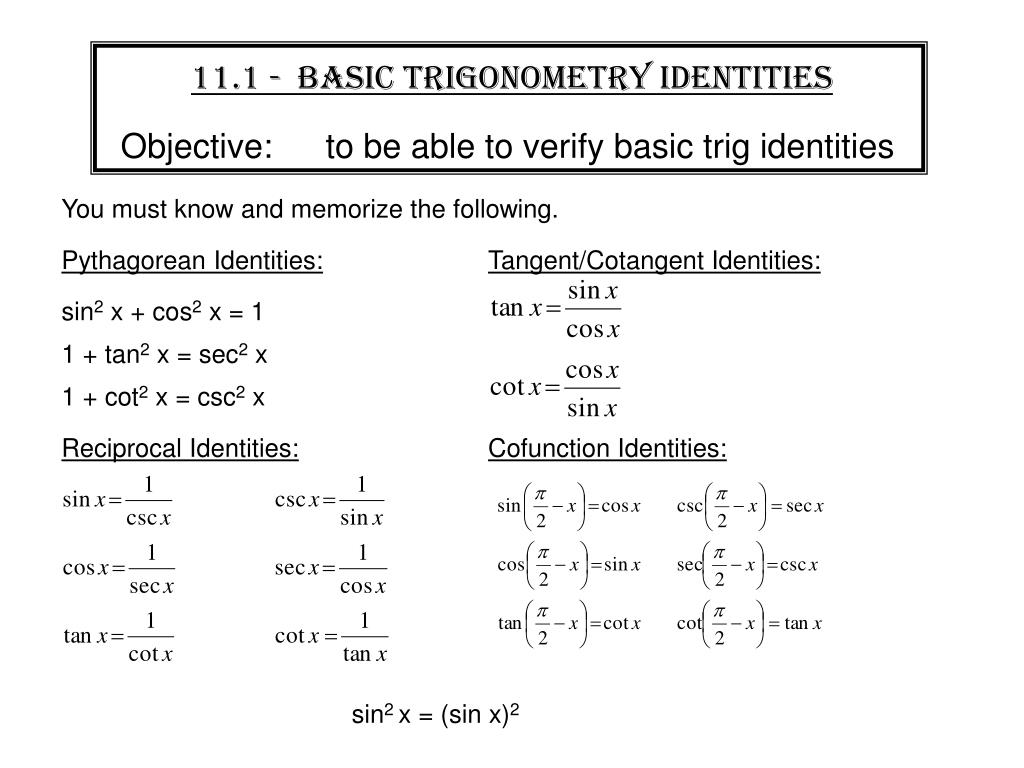
Ppt Warm Up Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

14 2 Trigonometric Identities
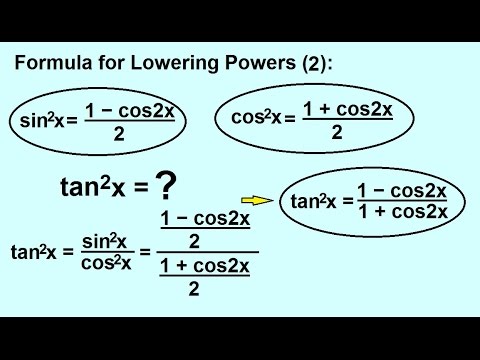
Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 29 Of 57 Formula For Lowering Power Tan 2 X Youtube
Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube

Cochranmath Solving Trigonometric Equations

Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia
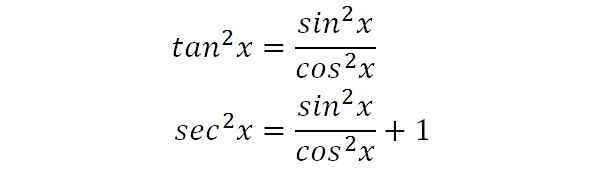
Integrate Sec 2x Method 2

Answered Verify The Identity 2 Sec T Sec Tcsc T Bartleby

10 4 Trigonometric Identities Pdf Free Download

Pdf Trigonometric Identities Formulas Lone tif Academia Edu

Trigonometric Addition Formulas From Wolfram Mathworld
Ch Ppt Download

Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download
Trig Identities Simplify Expressions Solutions Examples Videos

Summary Of Trigonometric Identities

Prove The Trigonometric Identity Tan 2 Theta 1 Cos 2 Theta 1 Math Introduction To Trigonometry Meritnation Com

Trigonometric Identity Problem Cos Tan And Sin Mathematics Stack Exchange
Prove This Identity Tan 2 0 1 Tan 2 0 Sin 2 0 Note I Pla
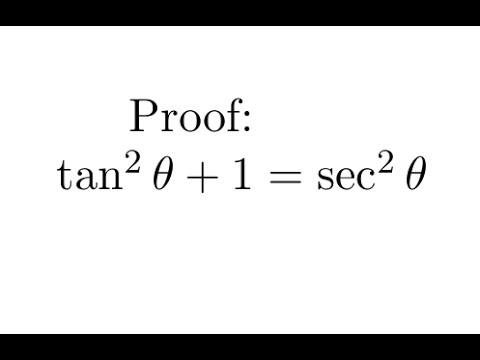
Proof Tan 2 1 Sec 2 Youtube

7 3 Sum And Difference Identities Mathematics Libretexts
Q Tbn 3aand9gctvddi Huq34sbenh4tuscml5fn7b4rgftjj3hnope Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrke K36wh6xkf2egm3xcjx80bjs V Ldzxr4b8yvatalqjq4zu Usqp Cau
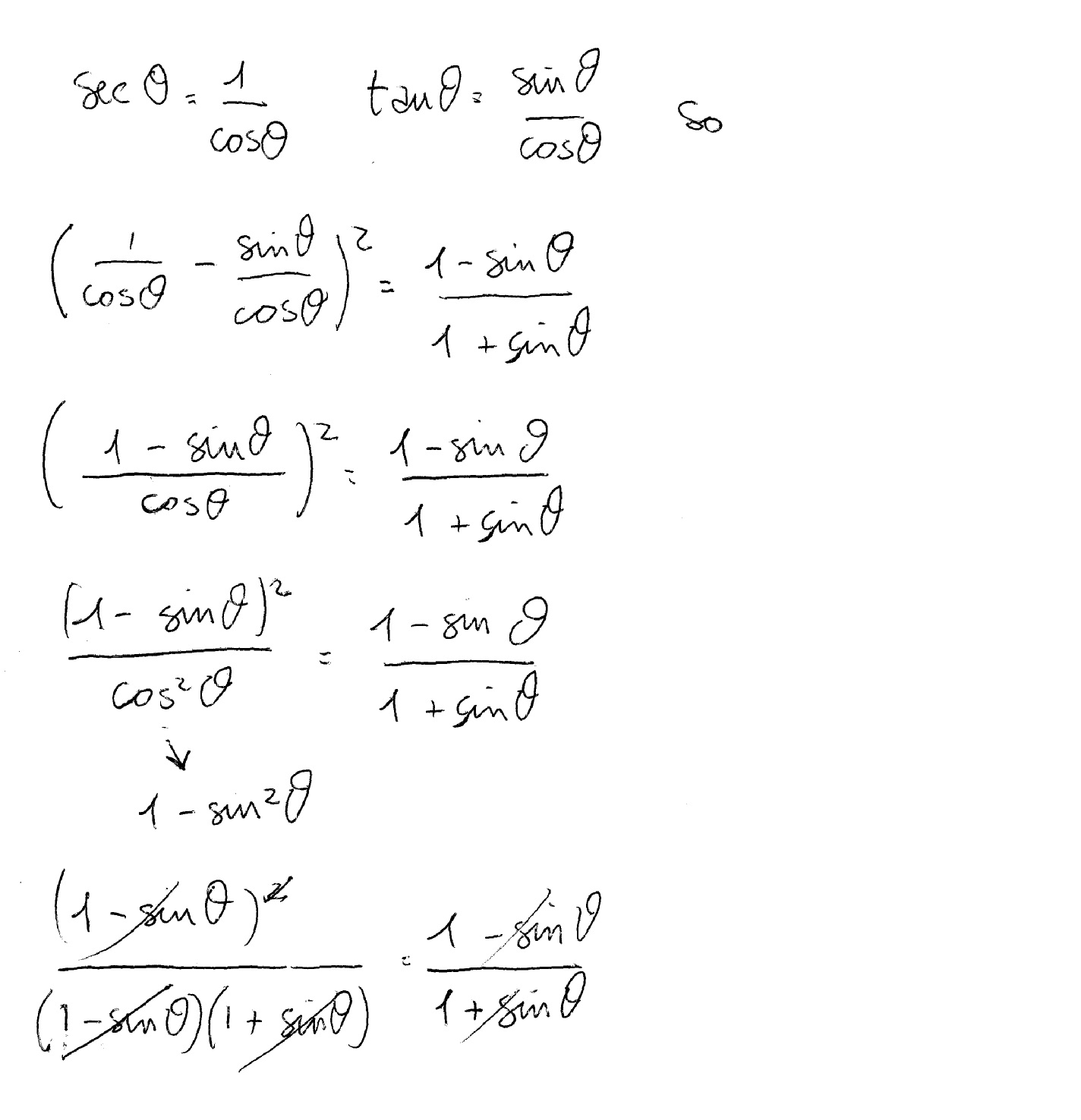
How Do You Prove The Identity Sectheta Tantheta 2 1 Sintheta 1 Sintheta Socratic

The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
Http Www Ecusd4 Com Vimages Shared Vnews Stories 59da5d1734f17 Pc 5 2 key Pdf

11 Basic Trigonometric Identities An Identity Is An Equation That Is True For All Defined Values Of A Variable We Are Going To Use The Identities To Ppt Download

Tangent Identities

Verifying Trigonometric Identities Process Make One Side Look
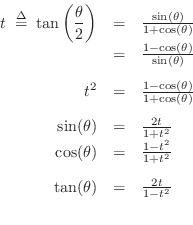
Complex And Trigonometric Identities Introduction To Digital Filters

Important Trigonometric Identiti

10 4 Integration Of Powers Of Trigonometric Functions

Oneclass Which Pythagorean Identity Is Correct A Sin 2 Theta 1 Cos 2 Theta B Tan 2 Theta 1 Sec 2

List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia

Trig Identities All List Of Trigonometric Identities Learn Trigonometry

General Solution Of The Trigonometric Equation Tan 2x Tan 23x Tan4x Tan 2x Tan 23x Tan4x Is

Trigonometric Identities 3 Sample Problems
2
7 Proving Ids Trig Functions Identities
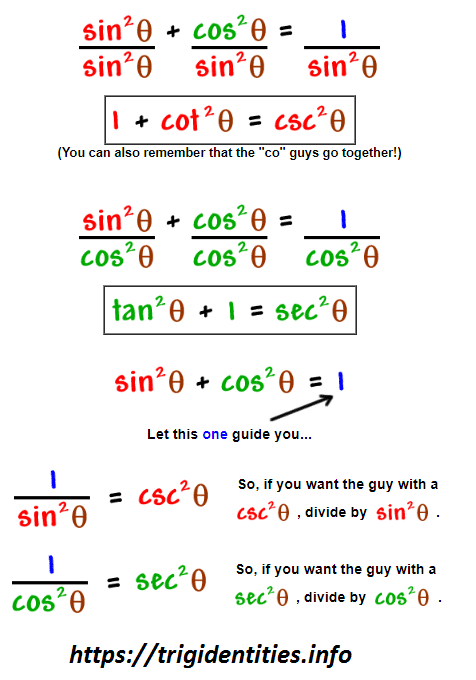
Pythagorean Trig Identities Recall Pythagoras Theorem Trig Identities

Ppt Verifying Trigonometric Identities Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Art Of Problem Solving

Justify The Pythagorean Identities
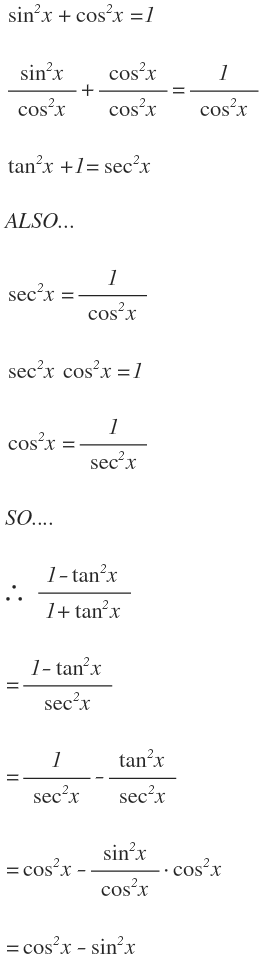
How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
Q Tbn 3aand9gctg1mv4zqwzzx9es1vyuwisok4cikumrujuyo2nyqlvyw5qkqqv Usqp Cau

Trigidentities1

Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 6 Trigonometric Identities Exercise 6 1 Get Pdf

Solved Verify The Identity 2 X Tan 2 X Esec X Tan X Sec Chegg Com

How Do You Verify The Identity Tan2theta 2 Cottheta Tantheta Homeworklib

Cochranmath Solving Trigonometric Equations

Trig Identities Worksheet With Answers 2

Trigonometric Identities

Solved Verify The Identity 1 Tan U 1 Tan2 U Cos N U Chegg Com

Tangent Identities

Trigonometry My Act Guide
2

Which Of The Following Expressions Completes The Identity 1 Sec 2 X Mathematics Stack Exchange

How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Homeworklib
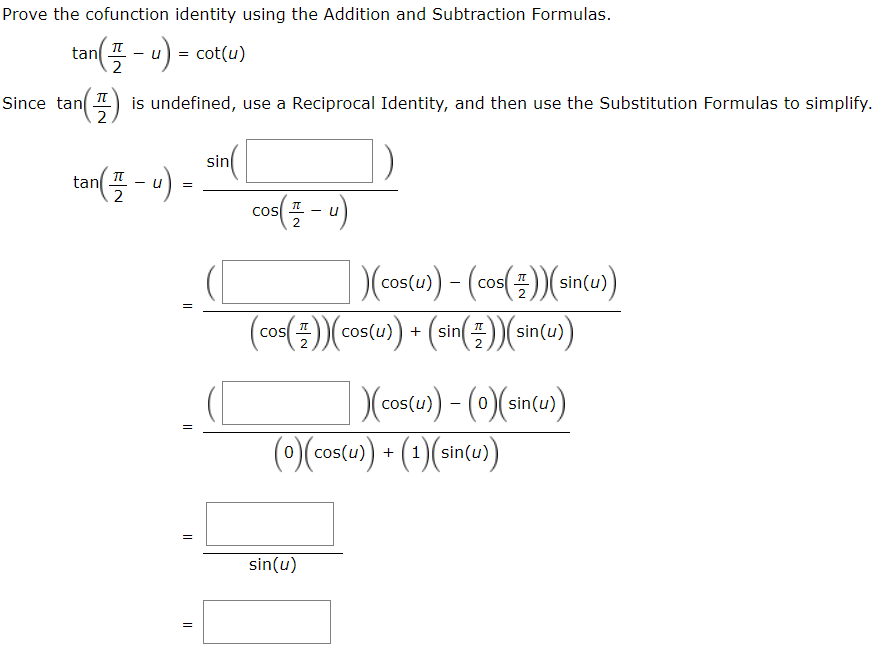
Answered Prove The Cofunction Identity Using The Bartleby

Trig Equations
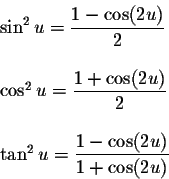
17 Power Reducing Identities Pre Calculus
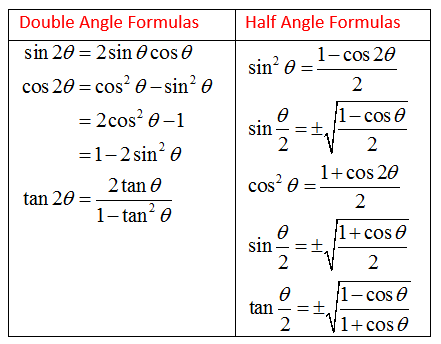
Half Angle Identities Socratic

Solved Prove The Given Identity Cos 2 Theta 1 Tan2 Th Chegg Com

Solved Verify The Identity Tan 2 0 1 Cos 2 1 Tan Chegg Com
Unit 3 5 1 Bingo Card

1 Trig Continued With Solutions Jackmathsolutions Com
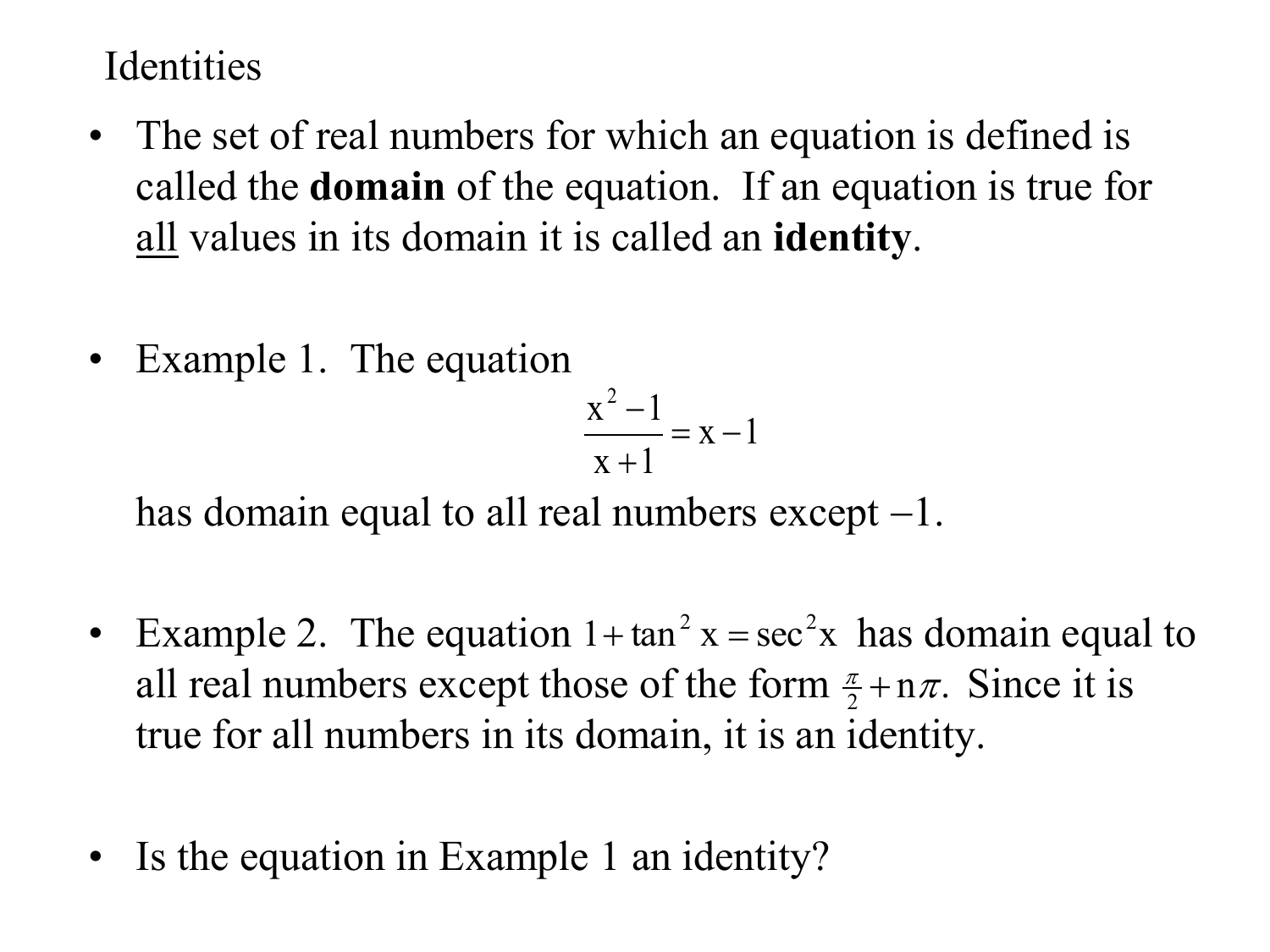
Identity

How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic

Trigonometric Identities 1 Conditional Trigonometrical Identities We Have Certain Trigonometric Identities Maths Solutions Identity Simplifying Expressions

Which Identity Needs To Be Used To Prove Tan Pi 2 X Cot X Brainly Com



