2px Differs From 2py Molecular Orbital In Which Of The Following
Sigma Pi Bonding Atomic Orbital Bonding Sigma S Pi P Bonds
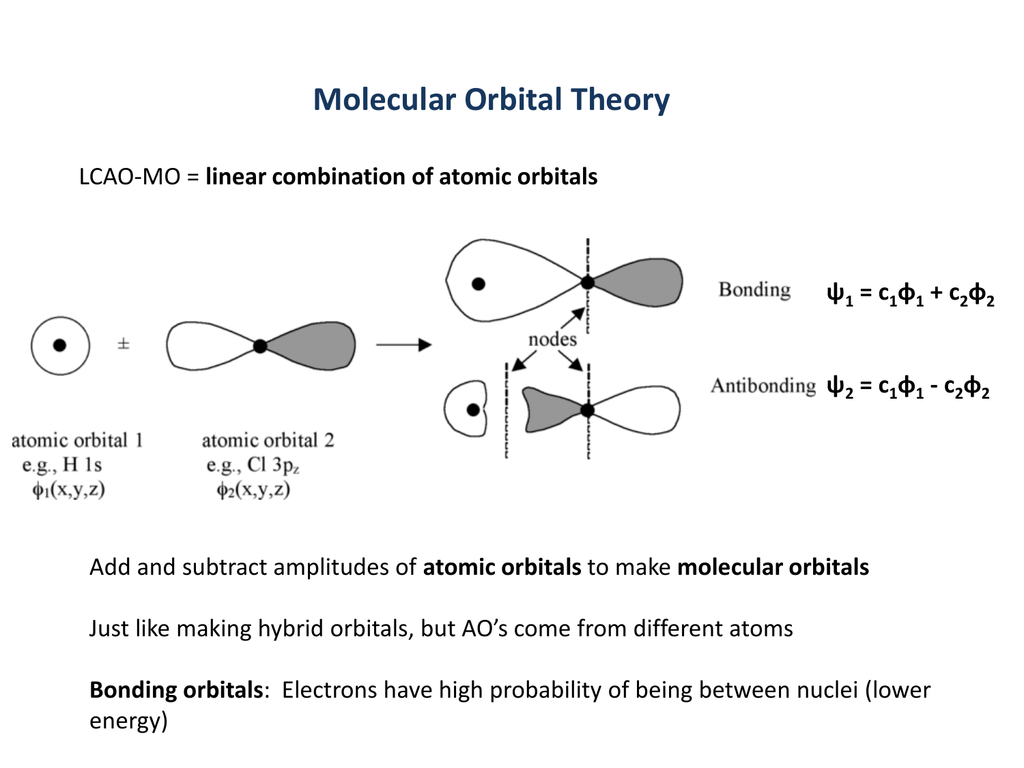
Bonding Orbitals

Ifas India S No 1 Life Science Chemical Science Net Gate M Sc Set Institute

Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Pi Bond Aromaticity A Pair Of Rings Transparent Png

Mo Theory

Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Describes Covalent Bonds In Terms Of Molecular Orbitals Which Result From Interaction Of The Ppt Download
KK (σ 2s) 2 (σ* 2s) 2 (σ 2pz) 2 (π 2px) 2 = (π 2py) 2.

2px differs from 2py molecular orbital in which of the following. Describe the hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in each molecule or ion. Which of the following species has the largest dissociation energy?. Specify the electron-pair and molecular geometry for each of the following.
J.D.Lee writes in his book Concise Inorganic Chemistry:. The molecular orbital configuration for O 2 molecule can be given as:. Principles of Chemical Science, Clicker Questions for Lecture 13:.
Label the atomic orbitals, MOs and identify the frontier orbitals. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Among the following molecular orbitals, how many have at least one nodal plane ?. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level.
MOLECULES Simplest would be HHe. σ *1s,σ 2s,σ *2pz,π 2px,π *2py,σ 2pz. Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridisation.
The interaction of four valence atomic orbitals on one atom (2s, 2px, 2py and 2pz) with a set of four atomic orbitals on another atom leads to the formation of a total of eight molecular orbitals:. B-Explain the differences in bond dissociation energies and bond lengths on addition and removal of an electron from NO. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals.
KK σ2s2 σ*2s2 π(2px)2 π(2py)2. The electrons are scattered from the crystal in different directions. See hundreds of plans.
If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the. Although MO calculations are beyond the scope this class we need to look at these for the simplest of molecules in order to understand the behavior of real molecules. Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic character of O2+ and O2-species.
Which of the following highlights a major difference between your molecular orbital diagram and the one calculated with Spartan (check all that apply)?. The end-to-end overlap of the 2px orbitals produces σ and σ* orbitals. Remember that the asterisks show the anti-bonding orbitals and the x, y, and zs all refer to the different sub-orbitals within the p-orbital.
It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures. Similarly for molecular orbital. On Monday's class, professor drew a MO diagram for O 2 molecule, and he concluded that the molecular orbital for O 2 is σ 2s 2 σ* 2s 2 σ 2pz 2 Π 2py 2 Π 2px 2 Π* 2py Π* 2px Assume that I did not copy it wrong, According to Lewis structure, O2 is O=O with 2 pair of lone pairs for each Oxygen molecule, so there should only be one sigma-bond and one pi- bond for each.
An alternative method for determining the symmetry of the molecular orbital is to rotate the orbital about the line joining the two nuclei and then rotate the orbital about the line perpendicular to this.If the sign of the lobes remains the same, the orbital is gerade, and if the sign changes, the orbital is ungerade. Are used for different shapes of electron cloud. Predict the valence electron molecular orbital configurations for the following, and state whether they will be stable or unstable ions.
This is an antibonding MO formed from a combination of 2p AO's on oxygen, so it is higher in energy than those atomic orbitals. Method) ( σ molecular orbital) :- It is formed by two ways –. Here we have provided NCERT Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 11.
Each O atom has the electron configuration He 2s² 2px² 2py 2pz. He - greater nuclear charge, electrons more tightly bound. How many molecular orbitals are produced by combining two atomic orbitals as illustrated in Model 1?.
According to MO theory;. Activity 23 —Molecular Orbital Model of Electronic Structure 155 Key quesTIons 1. The Molecular Orbital configuration of O2+ and O-2 is given below:.
The electronic configuration of C2 is :. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures. As a result, the atomic oritals loose their identity.
σ1s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2pz2 π2px2 = π 2py2π *2px1 O2-(17):. (The positions of atomic nuclei are indicated by the intersection of axis lines in each drawing.). The shape of the orbital depends on the quantum numbers associated with an energy state.
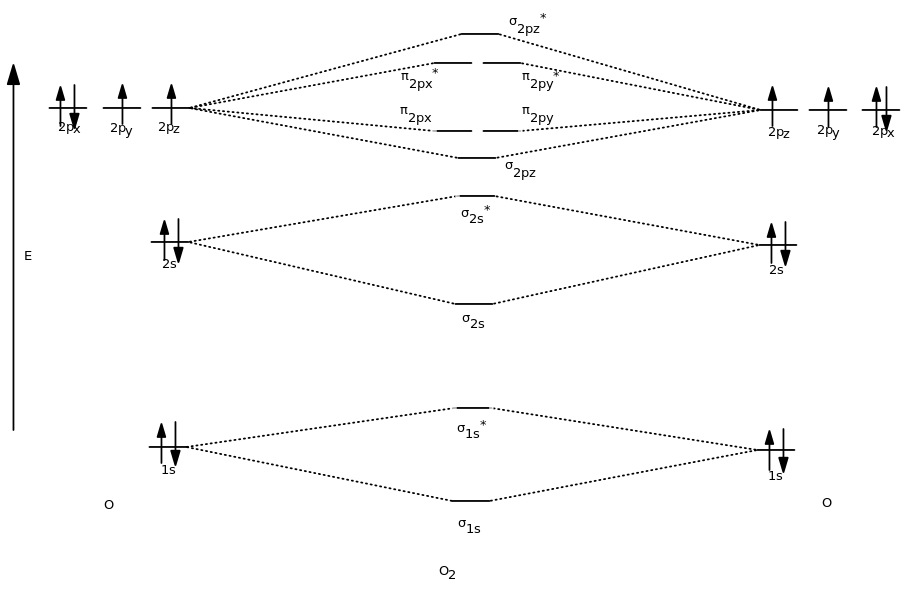
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. Browse modern house plans with photos. In the formation of C2 molecule, there will be evidently, 8 electrons to be accommodated in the molecular orbitals of C2.
(σ2s)2(σ∗2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px,π2py )4(π∗2px, π∗2py)2 On ionization, the electron will be removed from the highest-energy occupied MO (the HOMO), which is one of the degenerate π∗2px, π∗2py set. (i) NF 3 and BF 3 (ii) BF 4 – and NH 4 + (iii) BCl 3 and BrCl 3 (iv) NH 3 and NO 3 –;. Molecular orbital theory Author:.
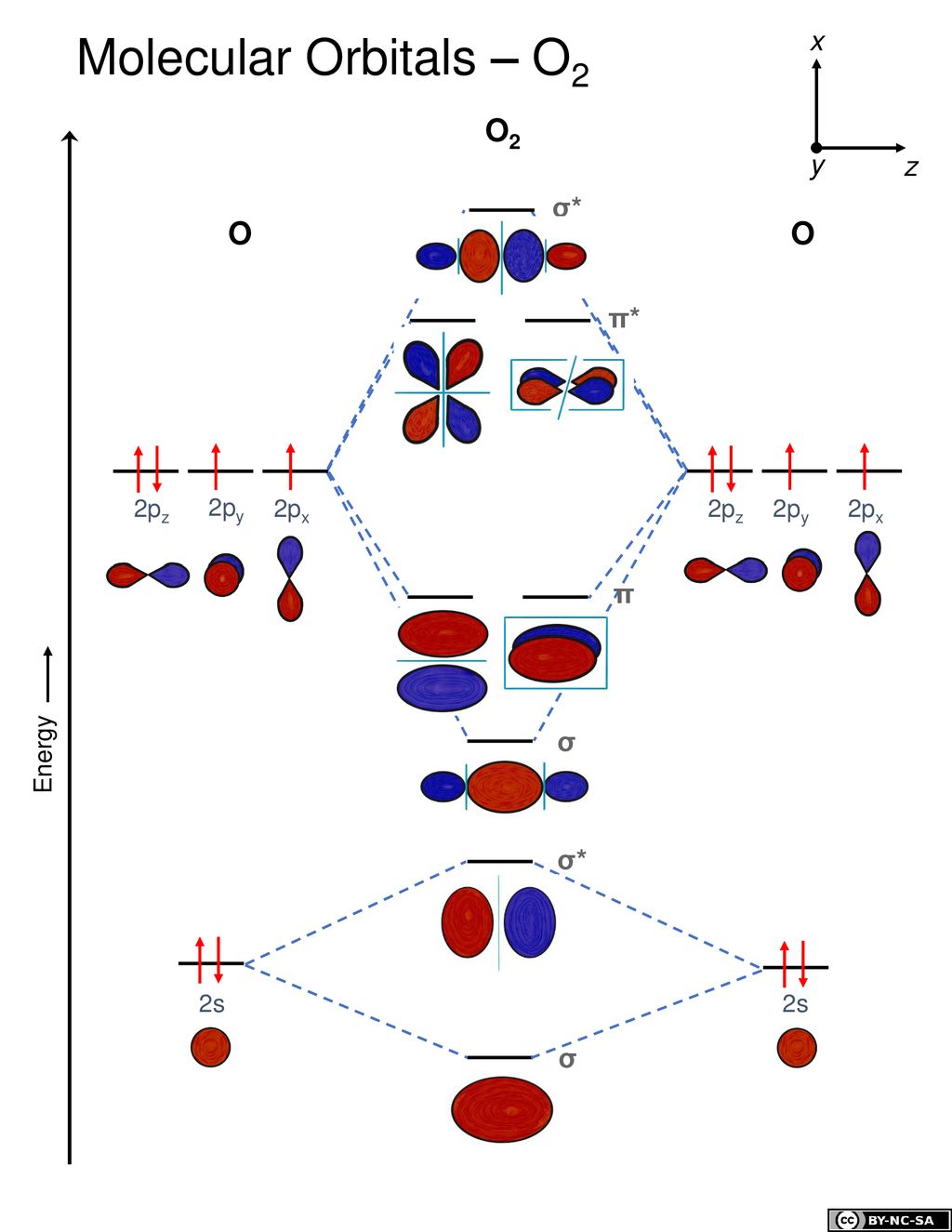
The increasing order of energies of various molecular orbitals is σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < (π 2px= π 2py ) <σ2pz < (π *2px = π*2py) < σ*2pz The important characteristic feature of this order is that the energy of σ2pz molecular orbital is. σ1s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2pz2 π2px2 = π 2py2π *2px2= π*2py1. From the electronic configuration of O2 molecule, it is clear that ten electrons are present in bonding.
Shapes of Molecular Orbitals (I.C.A.O. 28) The configuration (σ 2s) 2 (σ 2s *) 2 (π 2py) 1 (π 2px) 1 is the molecular orbital description for the ground state of:. Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule.
The 2s bonding orbital is not shown C. (However, He2 DOES not exist due to this destabilization) 11. It is paramagnetic as it contains two unpaired electrons.
O 2 – O 2 2– O 2 + O 2 2+ Which of the following statements is true?. So this energy difference between the HOMO and LUMO is termed the HOMO–LUMO gap. IV is false – two electrons in the bonding orbital are stabilizing.
Differs from H2 in two ways:. Question from very important topics are covered by NCERT Exemplar Class 11.You also get idea about the type of questions and method to answer in your Class 11th examination. This statement stand for highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), respectively.
There are actual energy values assigned to the orbitals. As there are unpaired electrons in π*(2px) and π*(2py) so it is paramagnetic (b)O2+ = total no.of electrons = 8 + 8 - 1 = 15 = sigma (1s) ^2 sigma*(1s)^2 sigma (2s)^2 sigma*(2s)^2 sigma (2pz) ^2 π(2px)^2 π(2py)^2 π*(2px)^1. Since this is just the location in which electrons can exert the most attractive force on the two nuclei simultaneously, this arrangement constitutes a bonding molecular orbital.
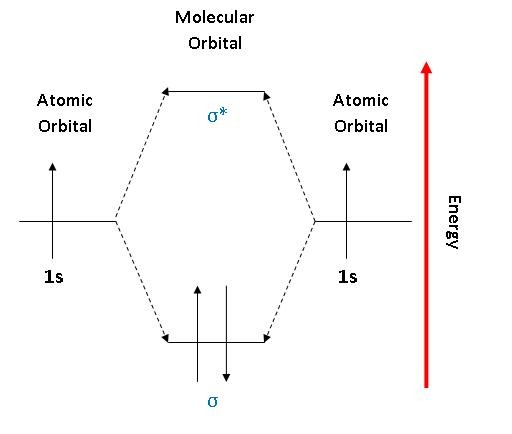
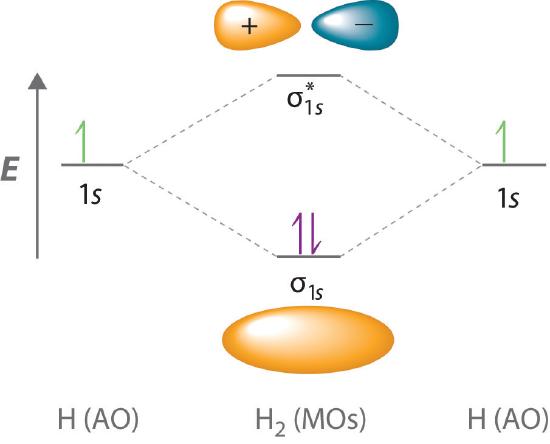
The energy degree that the bonding Molecular orbital is, is __higher/lower__ than the atomic orbitals from which it is formed lower the larger the positive overlap in the region between the nuclei, the __greater/lesser___ the drop in energy of the molecular orbital relative to the atomic orbital. If two s atomic orbitals from different atoms are combined, what are the names of the molecular. In molecular orbital (MO) theory we consider the orbitals to belong to the molecule, that is, the wavefunction is the quantum mechanical solution of the multinuclear molecule.
The configuration (σ 2s) 2 (σ 2s *) 2 (π 2py) 1 (π 2px) 1 is the molecular orbital description for the ground state of which of the following species?. B 2 2– C 2. σ1s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2pz2 π2px2 = π 2py2π *2px1.
Orbital with lower energy is called bonding molecular orbital and the other with higher energy is called anti bonding molecular orbital. The molecular orbitals are the energy states of a molecule, in. There are two columns labeled a and b B.
(2) Now three electrons to feed into m.o.'s. When two O atoms approach along the z-axis, the atomic orbitals overlap to form molecular orbitals. Molecular Orbital Theory O2 molecule The electronic configuration of oxygen is 1s22s22p4 The ground electronic configuration of O2 molecule, therefore, is - σ(1s)2 σ*(1s)2 σ(2s)2 σ*(2s)2 σ(2pz)2 π(2px)2 π(2py)2 π*(2px)1 π*(2py)1.
The letters KK are generally used for denoting the fully filled shells (K shells) in the two atoms. A.(σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 (π2p x) 2 (π2p y) 2 (σ2p z) 0 (π * 2p x) 0 (π * 2p y) 0 (σ * 2p z) 0 The molecular orbital valence electron configuration of the speciesC 2 is shown. The Molecular Orbital configuration of O2+ and O-2 is given below:.
The pairing in π 2px and π 2py or π *2px and π *2py will take place only when each molecular orbital of identical energy has one electron. The atomic orbitals combine (overlap) to form a new orbital known as molecular orbital. σ1s < σ * 1s < σ2s < σ * 2s < π2py = π2pz < σ2p < π * 2py = π * 2pz.
Li 2 + Be 2;. (σ1s) 2 (σ*1s) 2 (σ2s) 2 (σ*2s) 2 (σ2p z) 2 (π 2p x) 2 (π 2p y) 2 (π * 2p x) 1 (π * 2p y) 1. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ How many orbitals are having higher energy compared to σ2S for Li2 molecule from the molecular orbitals given below.
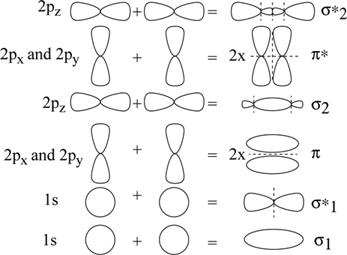
Watch walk-through video of home plans. 1s + 1s → σ(1s) and σ^★(1s);. π 2px π 2py π∗ 2px π∗ 2py MAR p.
O 2 = (σ1s) 2 (σ*1s) 2 (σ2s) 2 (σ*2s) 2 (σ2z) 2 (π2px 2 = π2py 2) (π*2px 1 = π*2py 1) Bond order = (N b-N a) /2 = (10-6)/2= 2. NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry is very important resource for students preparing for XI Board Examination. 29) The fact that O 2 is paramagnetic can be explained by:.
Determine the number of bonding electronsin the species C 2. Drennan, Catherine Created Date:. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in.
No different in energy (energy is conserved). σ1s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2pz2 π2px2 = π 2py2π *2px2= π*2py1. 2s< (π 2px, π 2py) <.
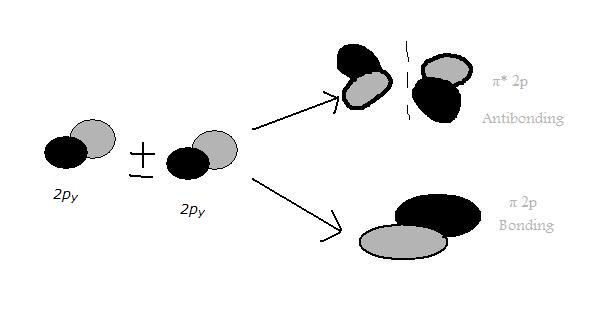
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. The bonding orbitals in dioxygen are σ, σ^★, π, and π^★ molecular orbitals (this editor will not allow me to use an asterisk symbol, so I will use a star instead). It is paramagnetic as it contains one unpaired.
N2^+ has two electrons in σ 2s, two in σ 2s *, two in π 2px, two in π 2py and one in σ 2pz. Energies for H, He different. Calculate the bond order for an ion with this configuration:.
Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic character of O 2+ and O 2-species. The p orbital is a dumbbell-shaped region describing where an electron can be found, within a certain degree of probability. Bond order in O 2 + = 10-5/2= 2.5 Bond order in O 2- = 10.
(σ 2s) 2 (σ 2s *) 2 (π 2px) 2 (π 2py) 2 (σ 2pz) 1. For instance, it has been observed experimentally that for molecules such as B2,C2 , N2 etc. As there is one unpaired electron in π*(2px) so it will be paramagnetic.
There is a significant difference between the energies of the 2s and 2p. The molecule or atoms have paired electrons in respective shell, this type of alignments diamagnetic. The Lewis structure of O 2.
Draw a molecular orbital (MO) energy level diagram for NO. 2s + 2s → σ(2s. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals.
Bond order O 2 + will form by removal of 1 electron from O 2.The electron will be removed from π * 2px or π *2py. MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY - Robert Mulliken (16-1986) valence electrons are. And bond order is 2.
As two H nuclei move toward each other, the 1s atomic orbitals of the isolated atoms gradually merge into a new molecular orbital in which the greatest electron density falls between the two nuclei. B.(σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 (π2p x) 2 (π2p y) 2 (σ2p z) 2 (π * 2p x) 1 (π * 2p y) 0 (σ * 2p z) 0 The molecular orbital valence electron configuration of. Study 33 Exam 4 review flashcards from Pascale L.
The 2px and 2py orbitals overlap side by side and produce two π orbitals of equal energy and two π* orbitals, also of equal energy. Electron configuration is (. (σ 2s) 2 (σ*2s) 2 (σ 2px) 2 (π 2py,π 2pz) 4 (π* 2py, π* 2pz) 3.
Among the given species identify the isostructural pairs. O 2 + = = (σ1s) 2 (σ*1s) 2 (σ2s) 2 (σ*2s) 2 (σ2z) 2 (π2px 2 = π2py 2) (π*2px 1) Bond order = 2.5. σ*1s, σ*2s, σ 1s, π 2py, π*2px, π*2pz, π2pz.
Molecular Orbital Theory of the Chemical Bond. σ 2s, σ 2s*, σ 2pz, σ 2pz*, π 2px, π 2py, π 2px*, and π 2py*. Only the two antibonding electrons are destabilizing.
How Might One Draw Atomic And Molecular Orbital Diagrams Socratic

Molecular Orbitals In Diatomic Molecules Youtube
Molecular Orbital Energy Of Antibonding M O Is Higher Than The Energy Of Atomic Orbitals

Which Of The Following Molecular Orbitals Has Two Nodal Planes
Diatomic Species Mo Theory Chemogenesis
Http Chemphys Armstrong Edu Nivens Generalchemistry Chapter10kotz Pdf
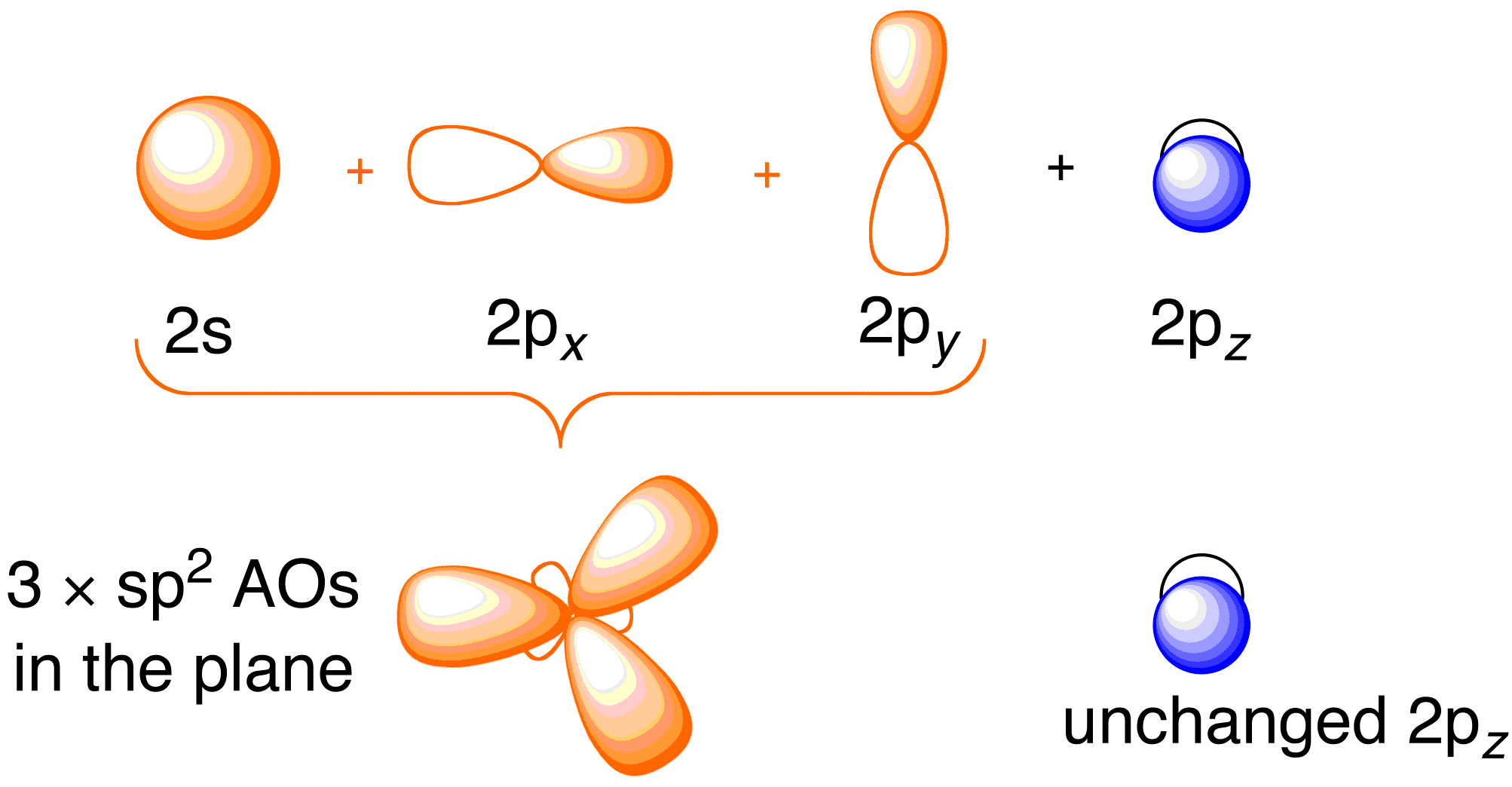
13 2 Molecular Orbitals For Ethene Organic Chemistry Ii

Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Describes Covalent Bonds In Terms Of Molecular Orbitals Which Result From Interaction Of The Ppt Download
Http Butane Chem Uiuc Edu Pshapley Genchem2 A6 Book Pdf
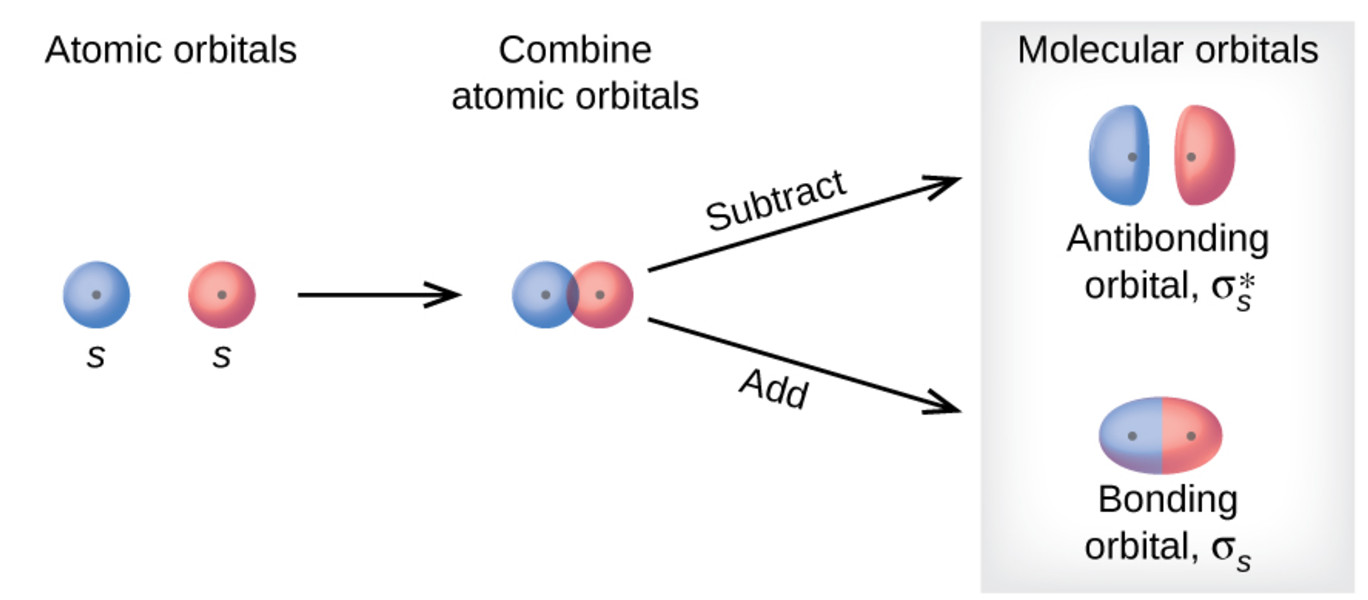
Types Of Molecular Orbital Formed Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11

Openstax Atoms First Chemistry 5 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Top Hat
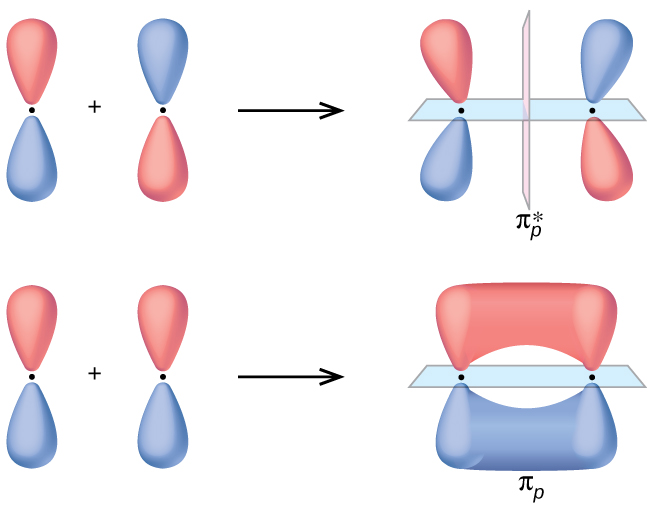
2 2 Molecular Orbital Mo Theory Review Chemistry Libretexts
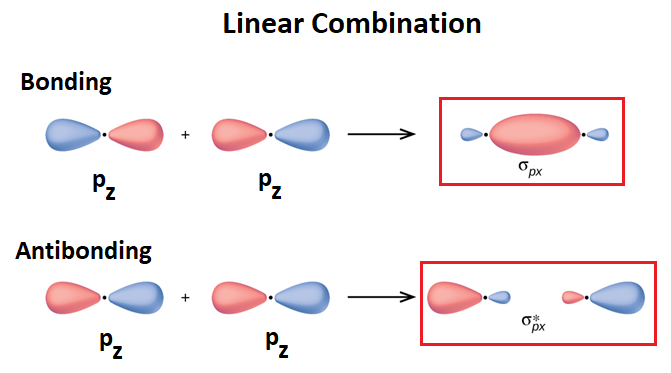
Sketch The Bonding And Antibonding Molecul Clutch Prep

Molecular Orbital Theory Mot Chemistry Study Material Emedicalprep Com Emedicalprep
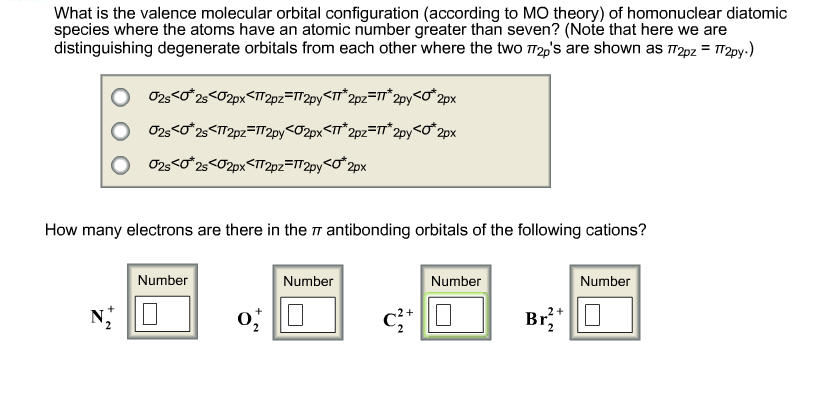
Solved What Is The Valence Molecular Orbital Configuratio Chegg Com

Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles
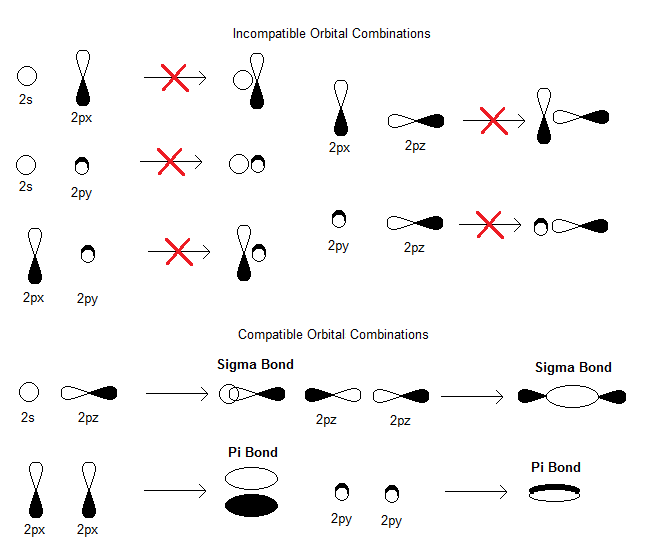
How Might One Draw Atomic And Molecular Orbital Diagrams Socratic

5 What Is The Bond Order In O2 6 Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For B2 The Number Of Unpaired Electrons In The B2 Molecule Is 7 Which One Of The Following

Inorganic Chemistry Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
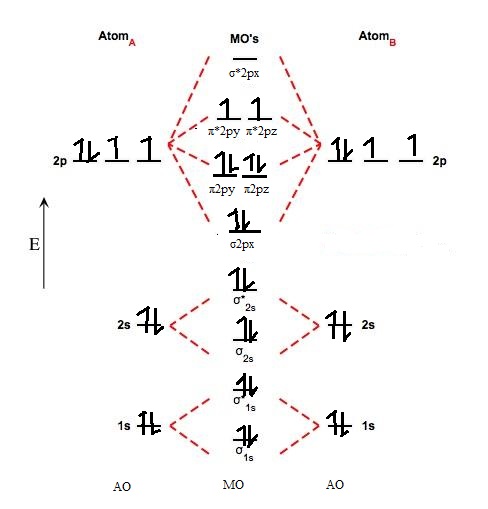
Molecular Orbital A Molecule In Which All The Electrons Are Paired Is Called Diamagnetic
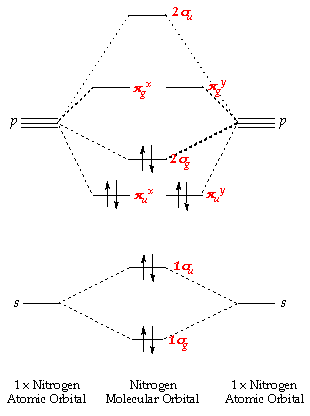
What Are The Molecular Orbital Configurations For N 2 N 2 2 N 2 N 2 And N 2 2 Socratic

Draw The Pictorial Representations Of The Molecula Chegg Com
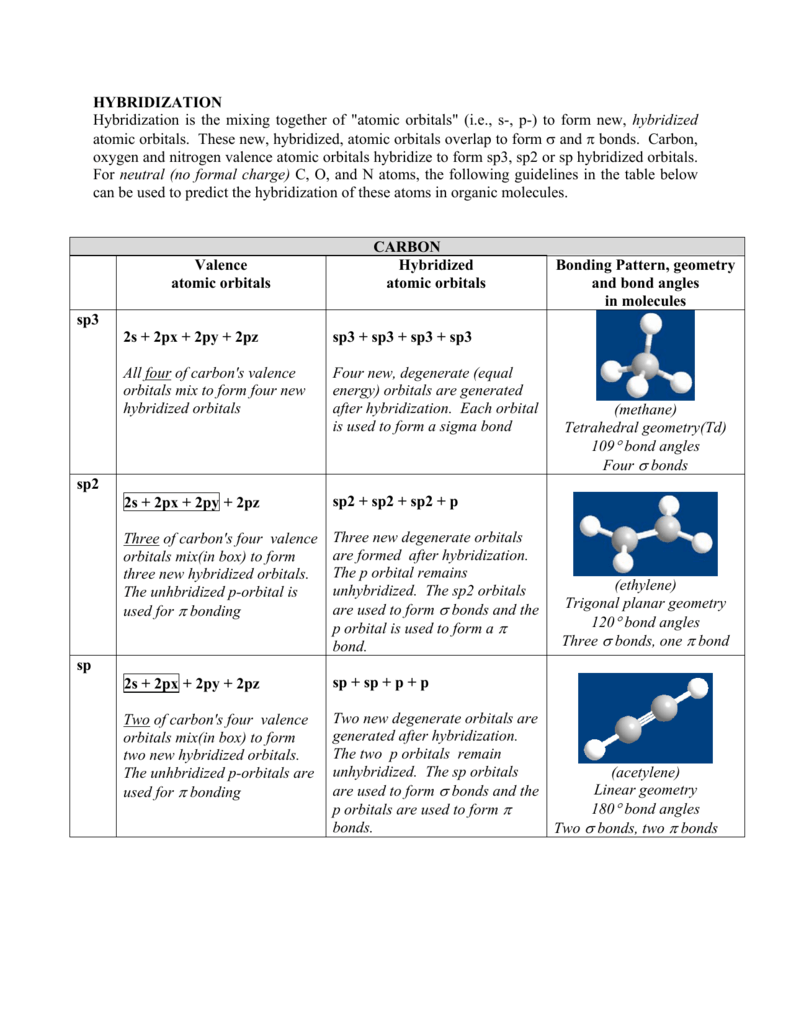
Hybridization Hybridization Is The Mixing Together Of Atomic
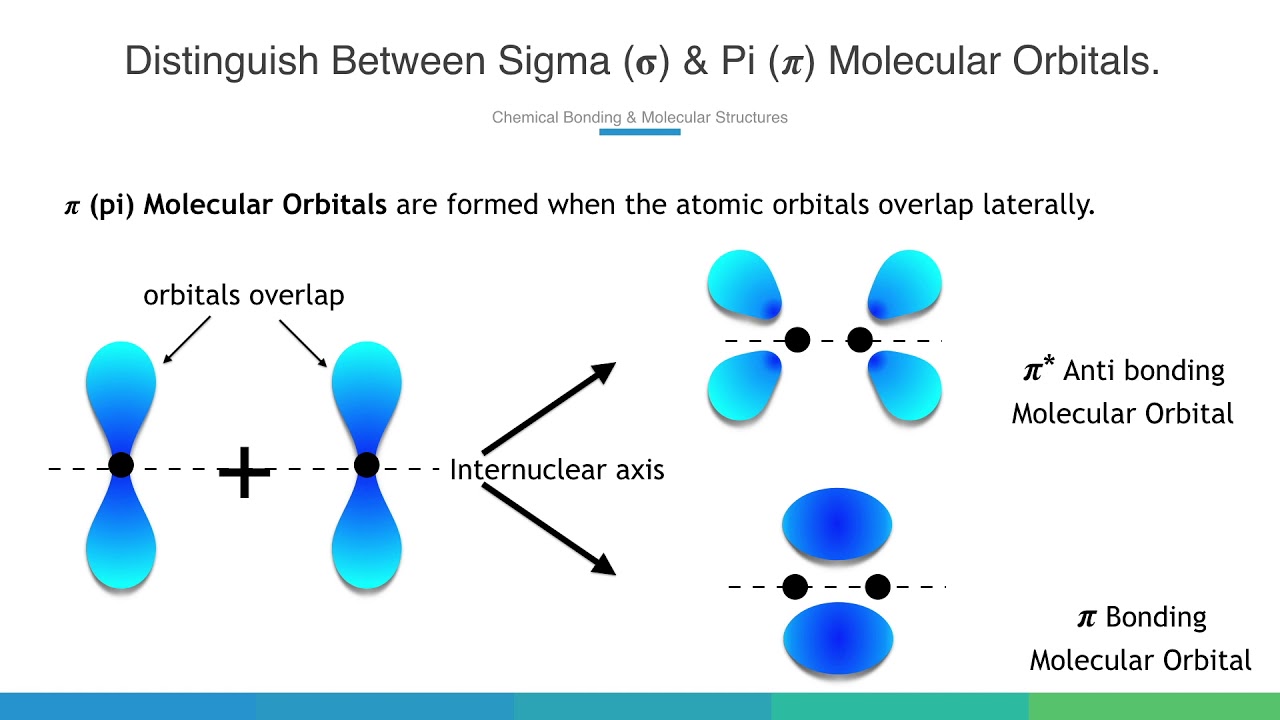
Molecular Orbitals In Diatomic Molecules Youtube

Which Of The Following Molecular Orbitals Has Two Nodal Planes

Help Understanding Anti Bonding Orbitals Could You Explain The Empty Box In This Diagram Chemistry

21 7 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts

What Is The Order Of Energies Of Various Molecular Orbitals Brainly In
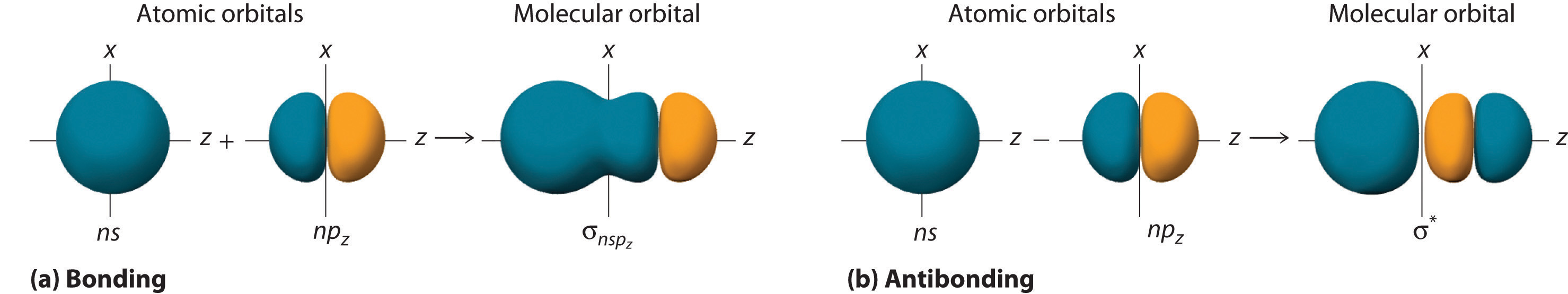
Molecular Geometry And Covalent Bonding Models
Www Chem Tamu Edu Rgroup Marcetta Chem362 Lectures Lecture 13 mo theory diatomics 17 Pdf
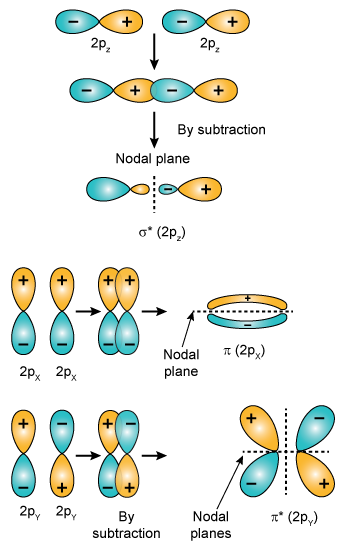
Which Of The Following Molecular Orbital Has Two Nodal Planes 1 2py 2 2s 3 2py 4 2pz Chemistry Topperlearning Com Yil5grcc

Inorganic Chemistry Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Thinfilmsliterature Files Wordpress Com 17 11 10 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Pdf

Class 11 Other Result Of Lone Pair Effect Freeguru Helpline
Molecular Orbital Theory Ppt Download
Http Butane Chem Uiuc Edu Pshapley Genchem2 A6 Book Pdf

Openstax Atoms First Chemistry 5 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Top Hat
Http Nanowires Berkeley Edu Teaching 104a 1411 13 Pdf

Orbital Diagrams For A The Cf X 2 P State And B The Cf A 4 S Download Scientific Diagram

Mo Theory
Http Www1 Lasalle Edu Prushan Ic Articles Polyatomic molecular orbital theory Pdf
Definition Of Molecular Orbital Theory Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcry Vts7dc6tpt4v Tcied Ve B9ondwookhju3qrfflwohmvrc Usqp Cau

Why There Is Difference In The Energy Levels Of O2 And N2 2px 2py And
Pictorial Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts
9 7 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
Http Stemwomen Org Teach Qm Qm58 Pdf
According To Molecular Orbital Theory 1s And 1s Overlap To Form Sigma 1s Bonding And Sigma 1s Molecular Orbital And So On Does This Have Any Relation To Sigma And Pi
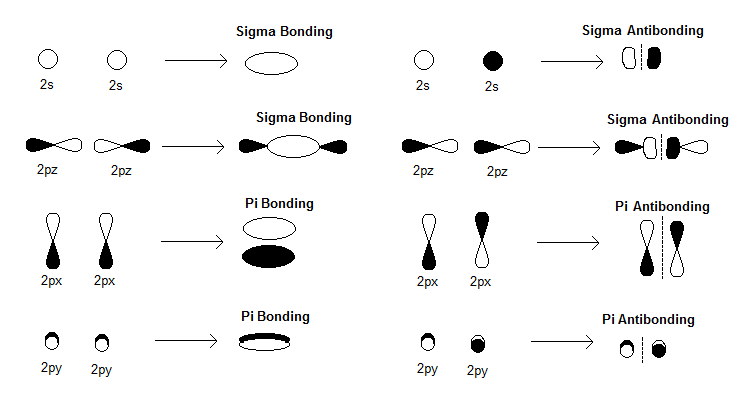
How Are There Pi Bonds In B 2 Molecule Without Sigma Bonds Socratic

Molecular Orbital A Molecule In Which All The Electrons Are Paired Is Called Diamagnetic
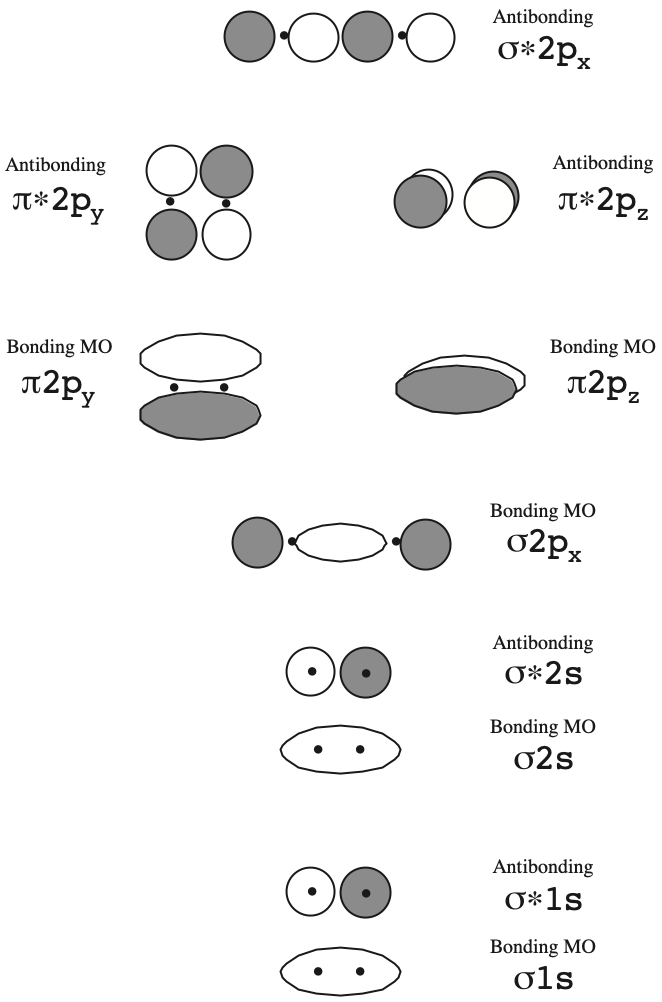
Diatomic Species Mo Theory Chemogenesis

2 Which Of The Following Overlaps Is Incorrect Assuming Z Axis Is Internuclear Axis 1

Zumdahlsamplech
Http Butane Chem Uiuc Edu Pshapley Genchem2 A6 Book Pdf
Molecular Orbital Theory Pranjoto Utomo
2
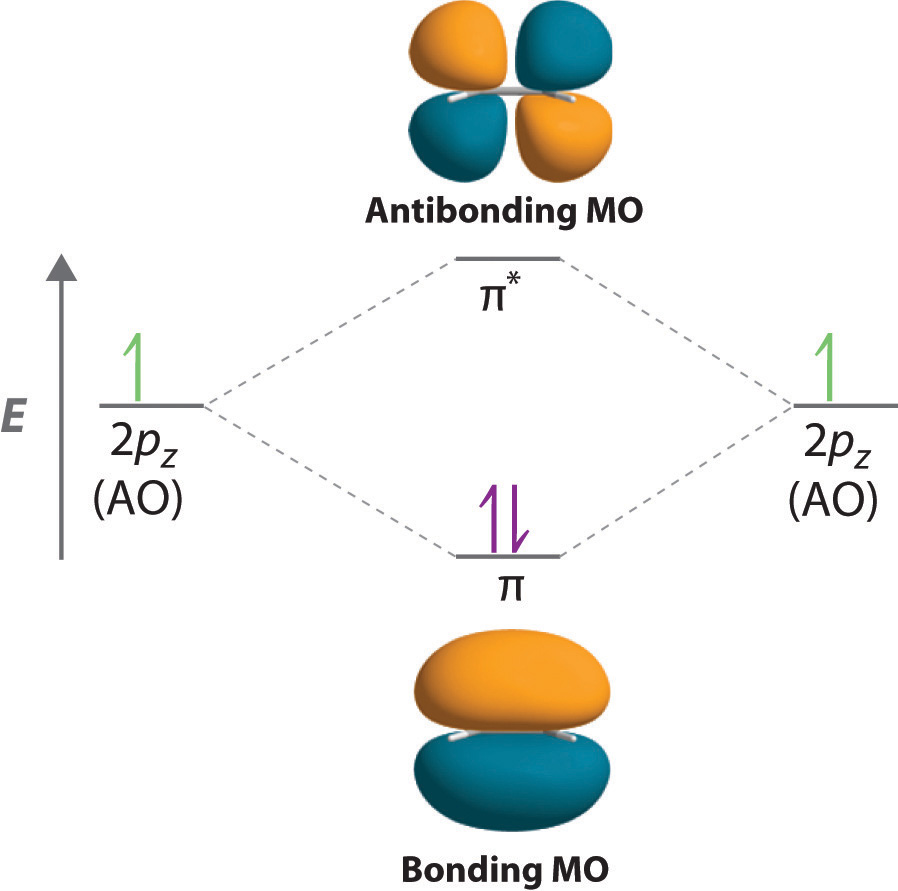
Molecular Orbital Energy Of Antibonding M O Is Higher Than The Energy Of Atomic Orbitals

How Do We Obtain The P Molecular Orbitals For Allene Via Huckel Theory Chemistry Stack Exchange

Ifas India S No 1 Life Science Chemical Science Net Gate M Sc Set Institute

Differentiated Chemistry

How Many Nodal Planes In Antibonding Sigma P Orbital Quora

Inorganic Chemistry Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
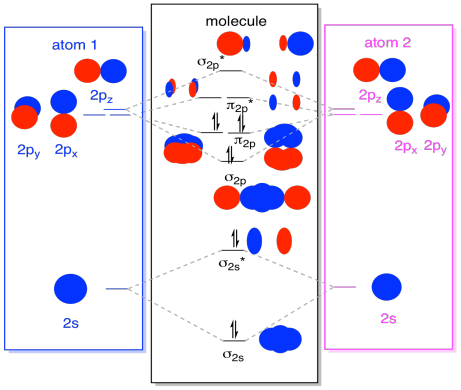
Structure Reactivity

Chapter04

Draw Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram Of O2 Molecule And Mention Its Bond Order Explain Why O2 Brainly In
Http Chemphys Armstrong Edu Nivens Generalchemistry Chapter10kotz Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq7ufxowzic9irhezeespst Rcp7c60lmhbb1xabhznwkqh8rnk Usqp Cau
Answer In Organic Chemistry Question For Ankit Q A

Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles

Molecular Orbital Theory
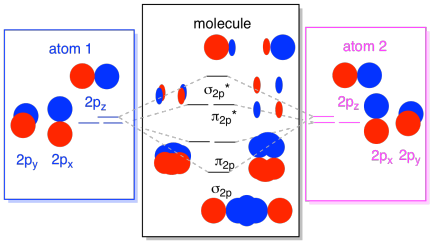
Structure Reactivity

Notation On Mo Diagrams Chemistry Stack Exchange

Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry For Majors
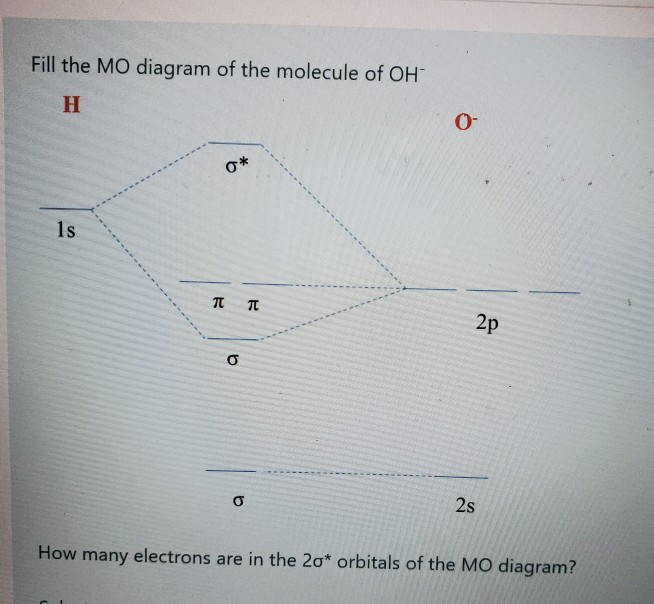
Solved Fill The Mo Diagram Of The Molecule Of Oh H P P 2p Chegg Com
Www Chem Tamu Edu Rgroup Marcetta Chem362 Lectures Lecture 13 mo theory diatomics 17 Pdf

1 Which Of The Following Order Of Energies Of Molecular Orbitals Of N2 Is Correct Brainly In
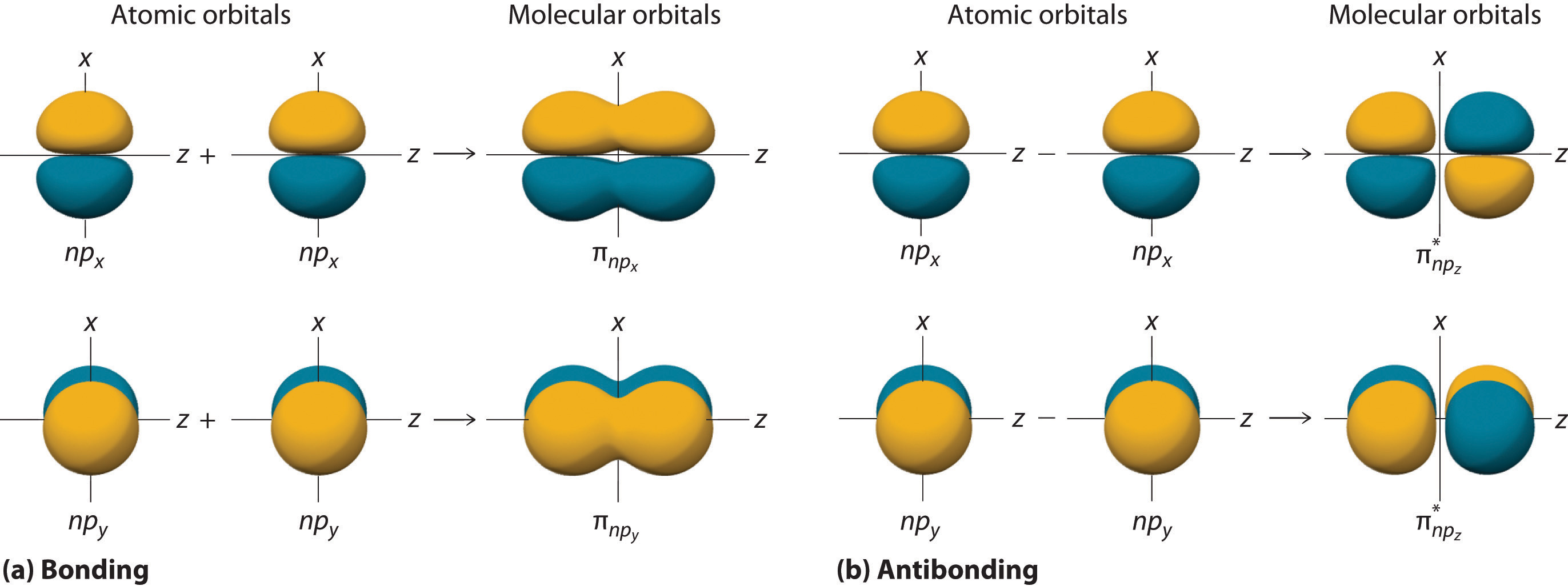
9 7 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
Www Chem Tamu Edu Rgroup Marcetta Chem362 Lectures Lecture 13 mo theory diatomics 17 Pdf
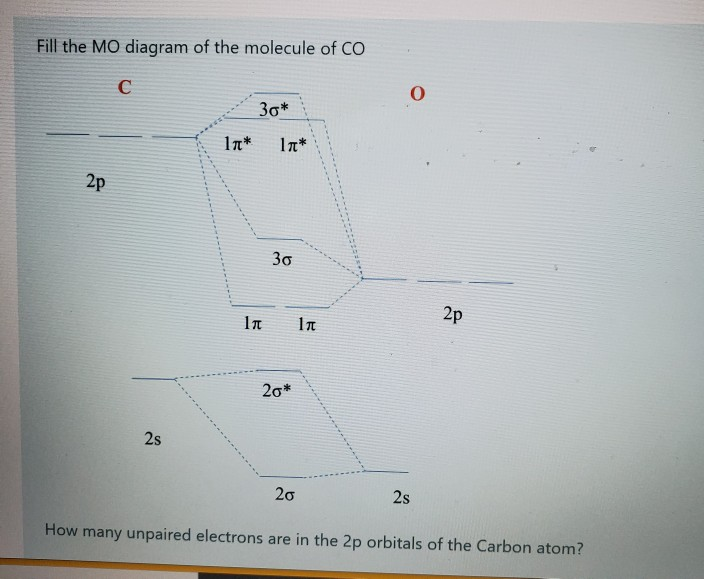
Solved Fill The Mo Diagram Of The Molecule Of Oh H P P 2p Chegg Com
Ciet Nic In Moocspdf Chemistry01 Kech Etext Pdf

In Which Mo Is The Overlap Of Atomic Orbit Clutch Prep
Www Chem Tamu Edu Rgroup Marcetta Chem362 Lectures Lecture 13 mo theory diatomics 17 Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gctaw3puv0frblx3unasd7 S5uogj Fhjrcwjqirax0cbmgvrsto Usqp Cau
Ciet Nic In Moocspdf Chemistry01 Kech Etext Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcss8waok3ahmxp5 Evk18etpm5tqyixradp5tvi0xljxvbchc Usqp Cau
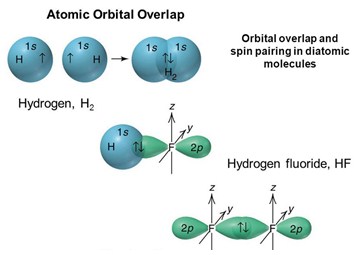
Shapes Of Molecules Molecular Orbital Theory A Level Chemistry Notes

Solved 5 A Quantum Chemistry Variational Calculation On Chegg Com

Pi Bonds And Sp2 Hybridized Orbitals Video Khan Academy
Consider The Following Molecules No No And No Using The Molecular Orbital Theory How Do You Evaluate Them In Terms Of Bond Energy And Stability Quora

Would Nodal Planes Of Participating Atomic Orbitals Be Nodal Planes Of Molecular Orbital Chemistry Stack Exchange

13 2 Molecular Orbitals For Ethene Organic Chemistry Ii

Using Molecular Orbital Model Sketch Or Describe The Interaction Of Two 2p Orbitals Be Sure To Homeworklib
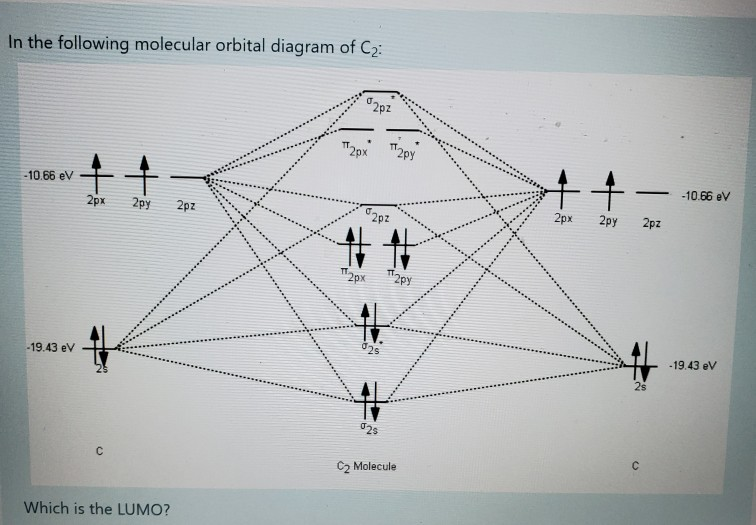
Solved Fill The Mo Diagram Of The Molecule Of Oh H P P 2p Chegg Com
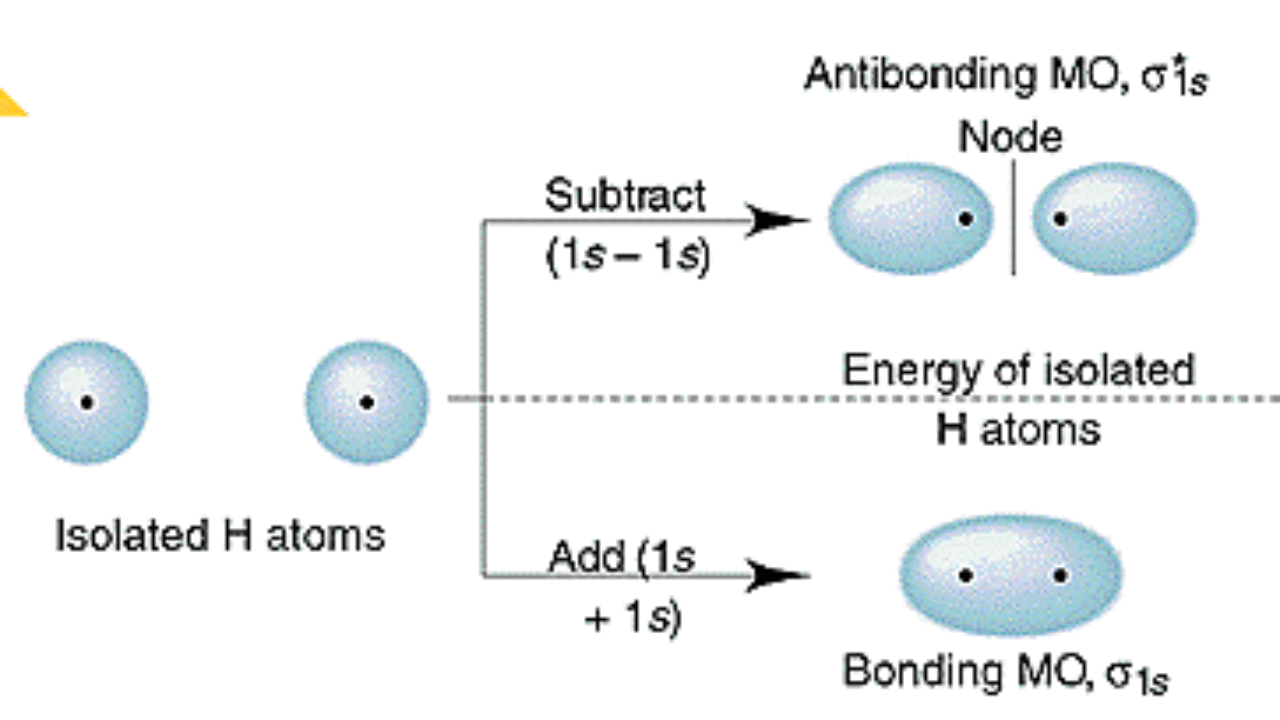
Molecular Orbital Energy Of Antibonding M O Is Higher Than The Energy Of Atomic Orbitals

Ps 1 C 1 F 1 C 2 F 2 Ps 2 C 1 F 1 C 2 F 2 Molecular Orbital Theory Lcao Mo Linear Combination Of Atomic Orbitals Add And Subtract Amplitudes Of Ppt Download
8 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry 2e Openstax
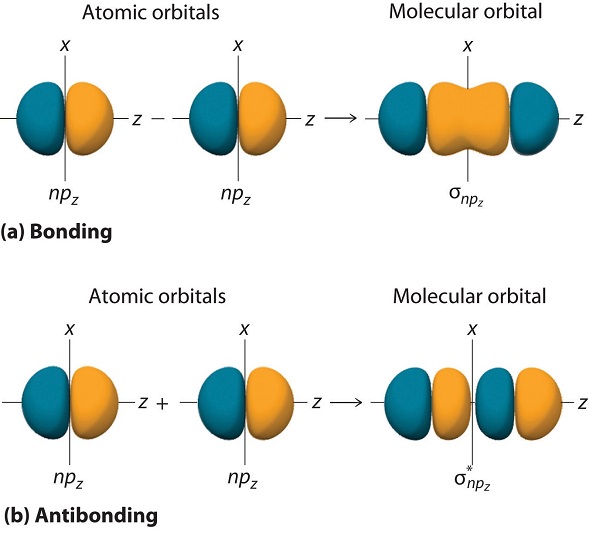
9 7 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
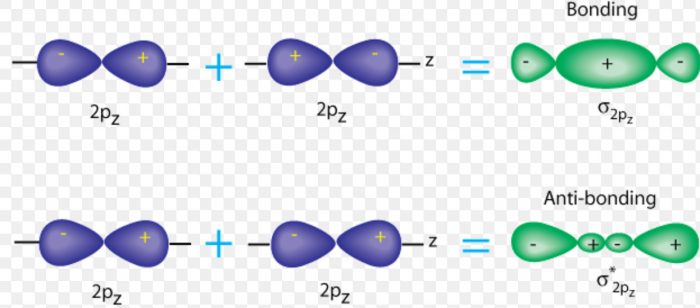
Types Of Molecular Orbital Formed Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11



