Odds Vs Relative Risk

Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table

Relative Risk Analysis And Odds Ratio Analysis

Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated

Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training

Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect

When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have.

Odds vs relative risk. In the statistics world odds ratios are frequently used to express the relative chance of an event happening under two different conditions. Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome. Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio.
This not being my area, naturally I turned to Wikipedia, which suggests that the odds ratio is commonly used for case-control studies, as odds, but not probabilities, are usually estimated whereas relative risk is used in randomized controlled trials and cohort studies. Even though odds ratios have more practical applications. Probability is the likelihood of an event in relation to all possible events.
The relative risk of picking a blue card in group A compared to group B is 1/3 or 0.33. Comment in Int J Epidemiol. Unfortunately, in some situations, you just have to get an OR, notably logistic regression and retrospective case-control studies.
Hazard ratio deals with a two part ( level ) explanatory variable and is an instantaneous risk over the course of the study. Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true. Carsten Oliver Schmidt 1 & Thomas Kohlmann 1.
It can also cause us to worry about the wrong things, especially when it comes to estimating our level of risk. These are all part of Survival Analysis a statistical method used in clinical trials. With a risk of dying due to atherosclerosis of 0.1 in , that is, one in a million, in the placebo arm and a 50% decrease in the risk of.
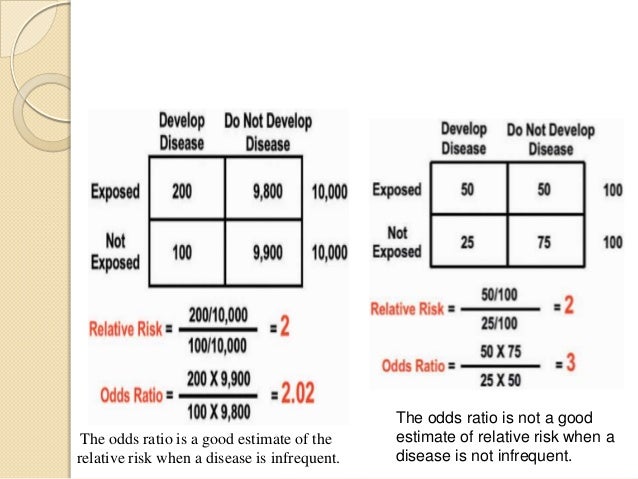
For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for. The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology. It has been proposed that the sample odds ratio is a good estimate of the population relative risk and can be interpreted as a relative risk when the disease or outcome is rare in the population, typically when the prevalence is less than 10%.
A 1 to 4 odds means there are five possible outcomes. However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio. Relative Risk Using.
The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds. A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group. A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group.
Such ratios are respectively called relative risk and odds ratio. Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that. Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other.
The risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed). The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (i.e. In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to pat.
The ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds). But since such perception is mostly correct, there is nothing (or almost nothing) wrong with that. Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration.
In a study on men given a new stati. The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure. We can understand that by looking at the picture.
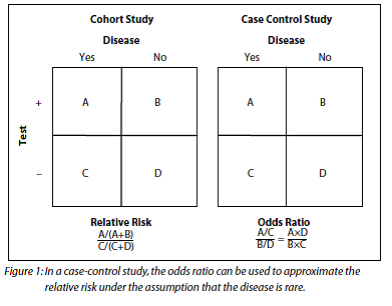
2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the non-obese:. In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio. Technically, relative risk should not be used to express results in case-control studies because the disease prevalence is not known and the apparent relative risk is dependent on the number of controls chosen.
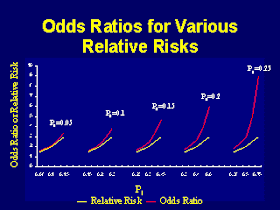
The home-made video abstract on the BMJ website shows you the difference between odds and risk, and how one odds ratio can mean several different relative risks (RRs), depending on the risk in one of the groups. Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (<10%), the odds ratio is close to the risk ratio. Interpretation of odds ratios and relative risk.
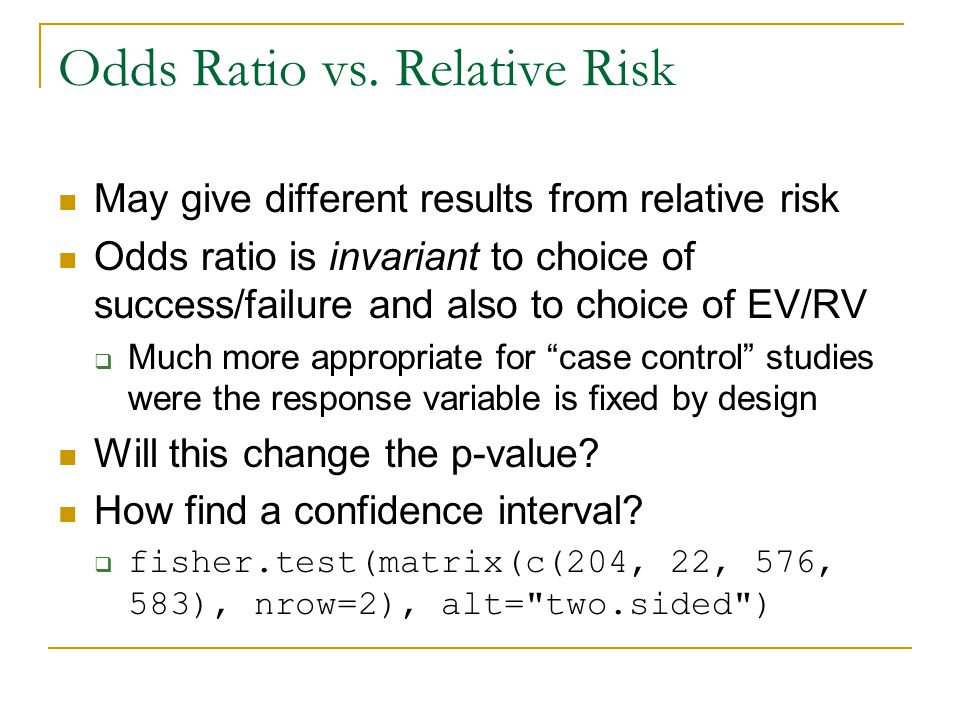
We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table. Important points about Odds ratio:. In the example above the risks would be 6 in 10 in the treatment group (6 divided by 10 = 0.6) and 3 in 10 in the control group (0.3), giving a risk ratio, or relative risk of 2 (0.6 divided by 0.3).
It’s worth stating again:. (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio). Therefore Relative Risk = the ratio (A/A+C)/ (B/B+D).
Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature. Odds while framing the relative vs absolute considerations. Odds ratio or relative risk for cross-sectional data?.
This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regression. It is the risk of a. In addition, if.
If action A carries a risk of 99.9% and action B a risk of 99.0% then the relative risk is just over 1, while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds with B. RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Whereas the absolute value of risk and odds is important in itself but the utility of these indices increases many-fold when their ratio is obtained relative to a comparison group. Odds Ratio (Case-Control Studies) The odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs.
4 However, the odds ratio is a reasonable approximation of the relative risk when the outcome is relatively rare (eg, when less than 1%. Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio. Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature.
In meta-analysis for relative risk and odds ratio, studies where a=c=0 or b=d=0 are excluded from the analysis (Higgins & Green, 11). 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (3.00 in those who are non-obese versus 1.29 in those who are obese). A group of 60 individuals with cancer are being evaluated to see they were exposed to a particular toxin X.
For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida:. For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have. Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese:.
A value greater than 1.00 indicates increased risk;. Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups. Relative risk and risk ratios (probabilitiy ratios) are different from odds ratios, although they might be close in certain cases.
Relative risk is a ratio of probabilities. A value lower than 1.00 indicates decreased risk. • When RR = 1, OR = 1 • When RR > 1, OR > 1 • When RR < 1, OR < 1 • The smaller the risk of the disease is in both groups, the closer the OR is to.
Certain types of trial designs, however, report risk as an odds ratio. Risk ratio or relative risk is a ratio of two “risks”. The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population.
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups. When to use the odds ratio or the relative risk?. If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same).
The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition. Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100. Vs ` = 10, !2 = 10!1 Odds and Odds Ratio 15.
OR is a bit more complicated and uses the formula A/ (1-A)/ B/ (1-B). The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk. The RR is much simpler to interpret and is most likely consistent with everyone’s intuition.
For example, in the context of a clinical trial comparing an existing treatment to a new treatment, we may compare the odds of experiencing a bad outcome if a patient takes the new treatment to the odds of. The odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs. Difference Between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk 1.
However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association. Fear is natural and healthy. Relative risk vs Odds ratio • They will always agree on the direction of comparison.
If a horse wins 2 out of every 5 races, its probability of winning is 2/5 (40%). If action A carries a risk of 99.9% and action B a risk of 99.0% then the relative risk is just over 1, while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds with B. Obviously, these results run counter.
When the outcome of interest is relatively rare (<10%), then the odds ratio and relative risk will be very close in magnitude. The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group. Literature Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research.
Relative risk vs Odds Ratio vs Hazard Ratio. Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another. RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies.
For a retrospective design called a case-control study, the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti 02).In a case-control study, two independent samples are identified based on a binary (yes-no) response. Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Non-fatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878. In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable.
■ An RR or OR of 1.00 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups. Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio. Your odds of dying from an accidental opioid overdose continue to be greater than dying in a motor-vehicle crash.
If you are interested in the blue card, it happens once among those five outcomes, or % of the time. The direct computation of relative risks is feasible if meaningful prevalences. The comparison group generally is the control group.
To understand Odds Ratio now, lets go through another but similar example. Covariate adjustment is eas …. The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it’s that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR). Likewise, relative risk makes a lot of sense. It can help us respond to danger more quickly or avoid a dangerous situation altogether.
When comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference. Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds. Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (i.e.
In such a case, investigators often interpret the odds ratio as if it were a relative risk (i.e., as a comparison of risks rather than a comparison of odds which is less intuitive). Therefore, the odds of rolling four on a dice are 1/5 or %. For a retrospective design called a case-control study, the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti 02).In a case-control study, two independent samples are identified based on a binary (yes-no) response variable, and the conditional.
Relative risk should not be confused with absolute risk, which in this case is 25/100 or 25%, or 1 in 4. Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a non-exposed group. A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group.
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 9.2.a). I just remember that odds ratio is a. For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uni.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Www Nwcphp Org Docs Risk Risk Transcript Pdf

Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey

Measuring Of Risk

Epidemiologic Principles Oncohema Key

Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Proport Chegg Com

Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals

Math3010 Week 6

Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia

Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau

Biostatistics Series Module 8 Assessing Risk Hazra A Gogtay N Indian J Dermatol

The Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Comparing Download Scientific Diagram
On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect

Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
Excel Odds Ratio Foodborne Disease Outbreak Toolkit

Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
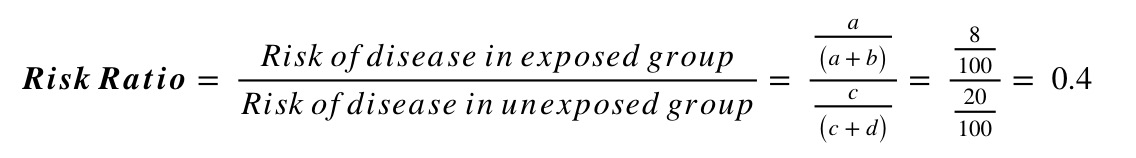
Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge

Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking
Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo
Mara Averick As Someone Who Asks For Odds Ratios And Relative Risk At The Vet I This Post How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A

Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh

Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough

Pdf Understanding Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Related Terms As Simple As It Can Get Semantic Scholar

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean

Image Result For Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Risk

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download

Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout

How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology

Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id

Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research

Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar

Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1

Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To

Literature Search
Relative Risk Wikipedia

Epidemiology Stepwards

I Pinimg Com Originals 6b 2a 35 6b2a35e8cd21a98
Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download

Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk

What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal

Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Rati Chegg Com
Behavioral Flashcards Memorang
Requesting Effect Measures

Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
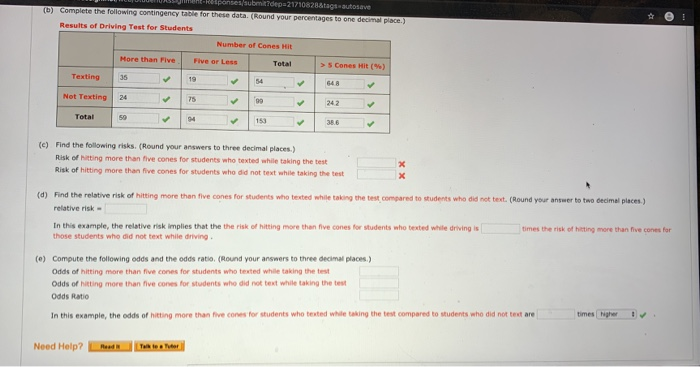
Solved Contingency Table And Risk Relative Risk Odds A Chegg Com

Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect

Xmlinkhub

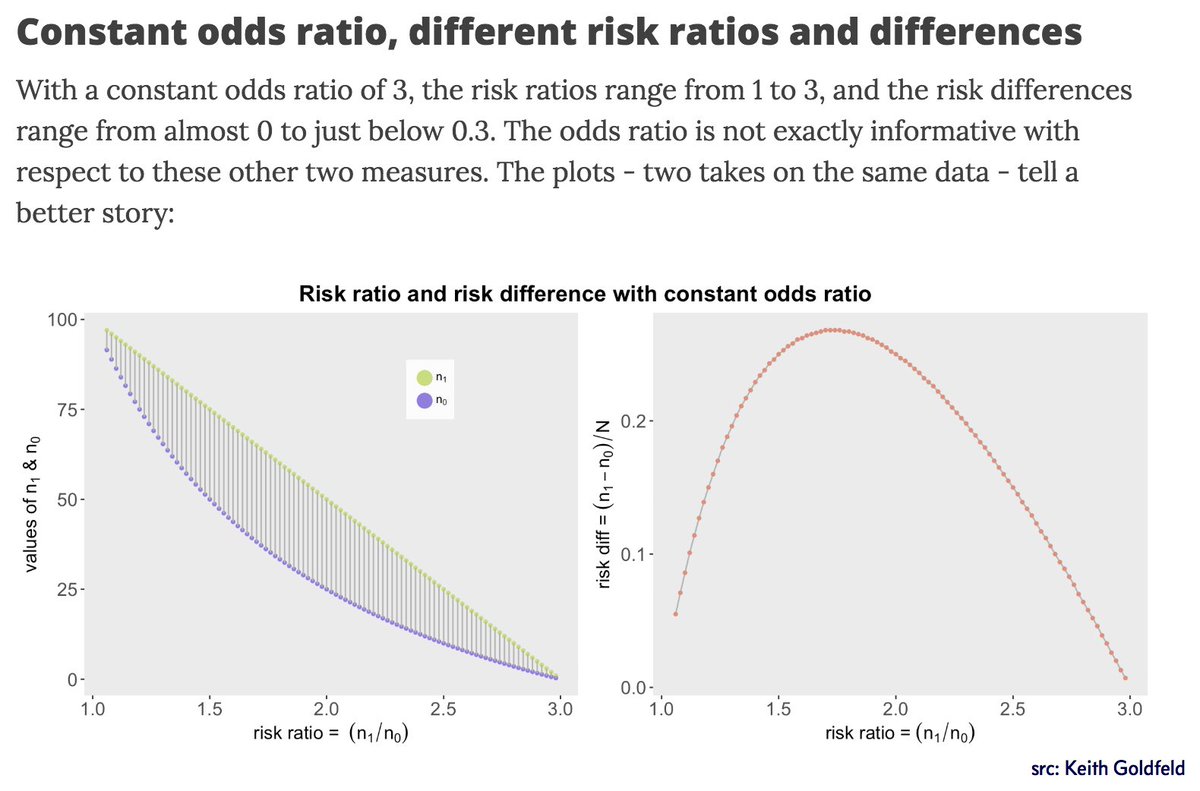
Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
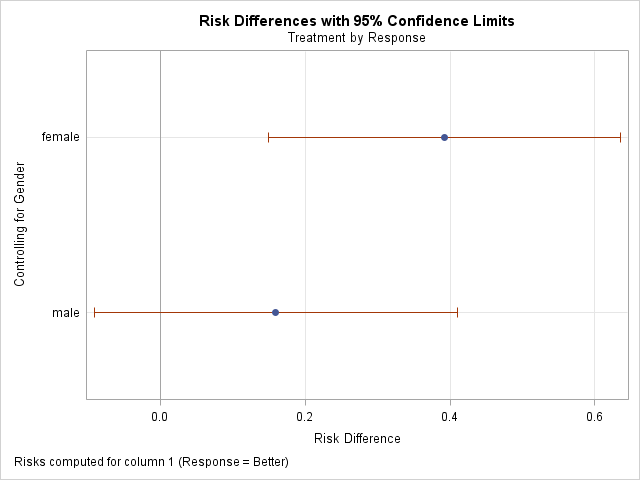
Risk Differences Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Plots With Proc Freq
1

Ppt Categorical Variables Relative Risk Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
2
Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com

Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
6

Relative Risk Odds Ratio

1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table

Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo
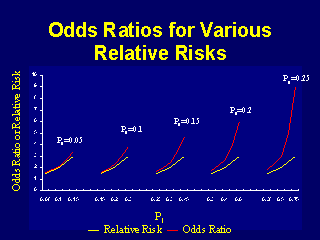
On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk

Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
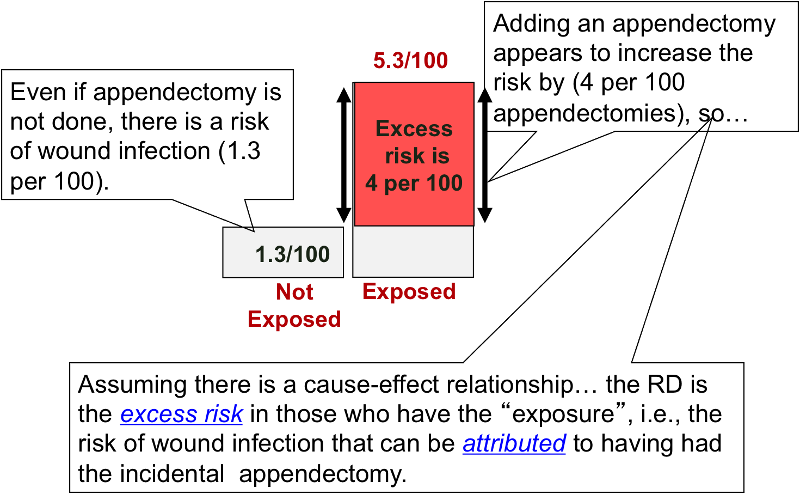
Risk Differences And Rate Differences
24
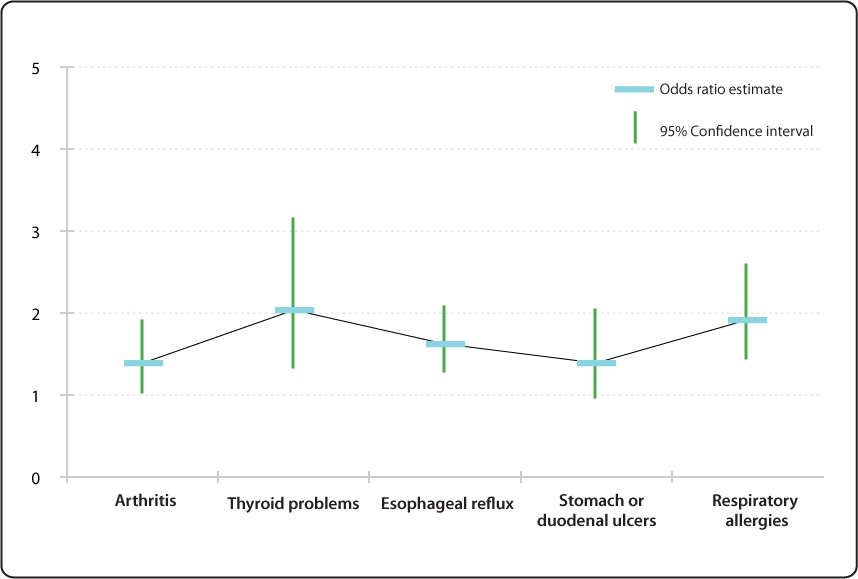
Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd

Glossary Of Research Terminology
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnh1uw23gmkmgfg0omhxyeez8cwvljdyhd6xi8w J Un51itbu Usqp Cau
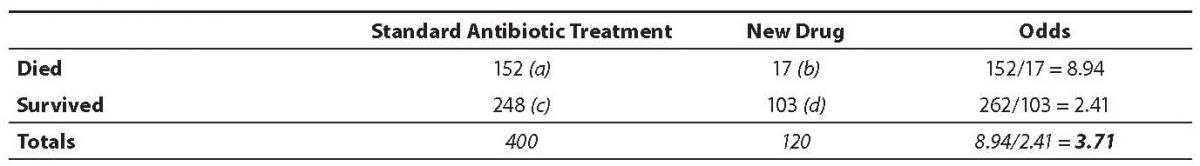
The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau
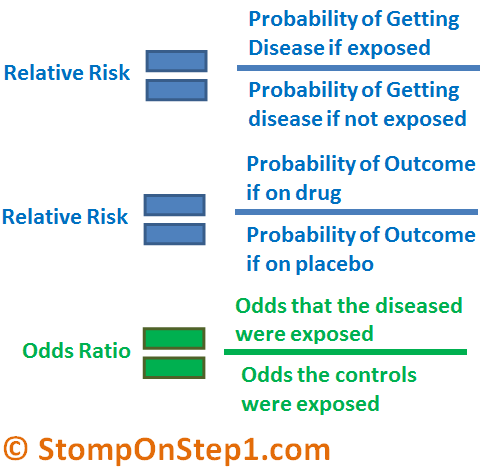
Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor

Statistc 111 Lecture Notes Spring 19 Lecture 11 Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ert2

How To Calculate Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Google Search Odds Risk Calculator

Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream

Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj
Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo

Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

How To Calculate Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Google Search Odds Risk Calculator

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True

What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora

First Aid Epidemiology Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet

Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
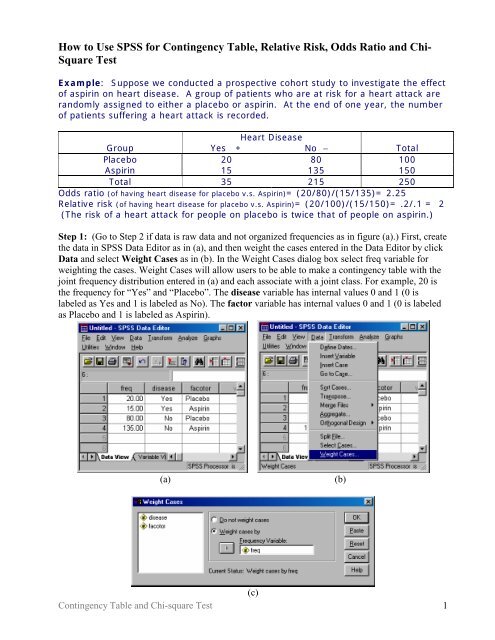
How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio

Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction
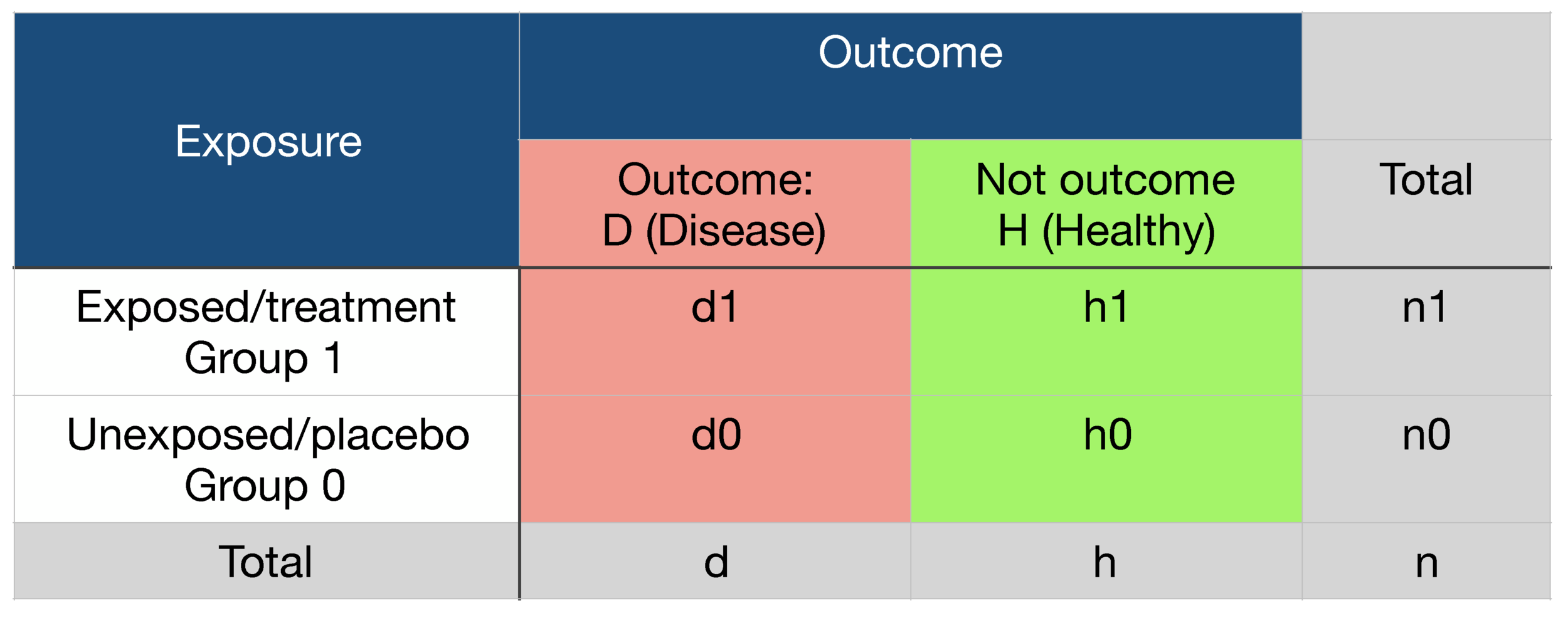
Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj

Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube

Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1

Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases
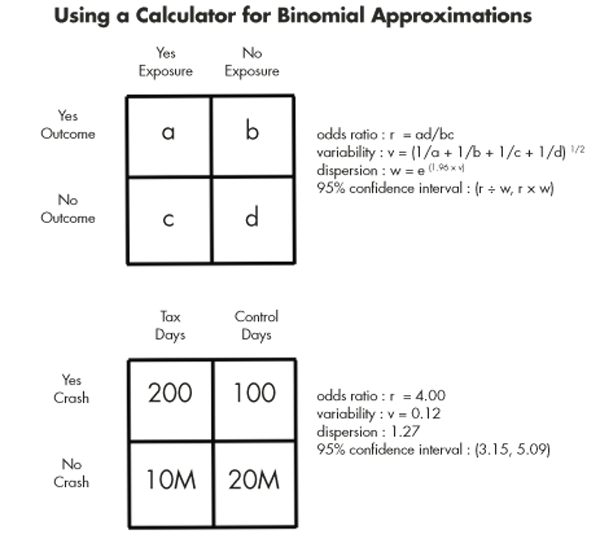
Can Tax Deadlines Cause Fatal Mistakes Chance



