Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
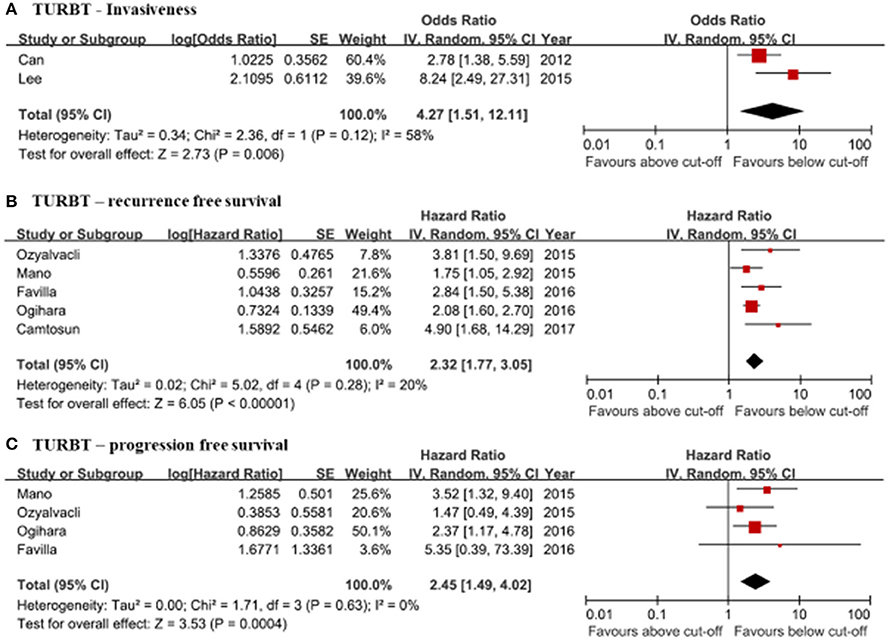
Frontiers Clinical Significance Of Pre Treated Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In The Management Of Urothelial Carcinoma A Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Oncology

Glycemic Variability And Diabetes Complications Does It Matter Of Course It Does Diabetes Care
Plos One Trans Fatty Acids In Adipose Tissue And Risk Of Myocardial Infarction A Case Cohort Study
2
Cov(u j,b j) = ρστ.

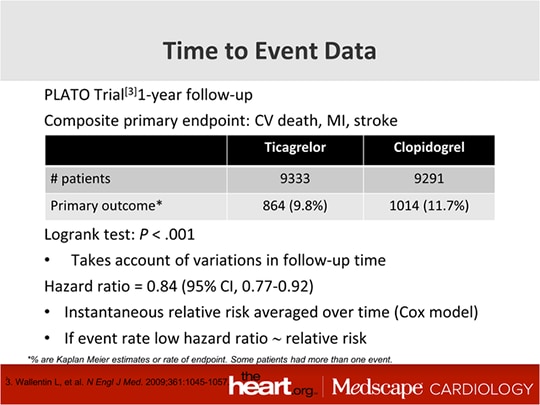
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio. If a horse wins 2 out of every 5 races, its odds of winning are 2 to 3 (expressed as 2:3). Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each other. Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof.
The point estimates for odds ratios for dementia outcomes associated with reading Japanese were all greater than 1.0;. The odds ratio should not be confused with relative risk or hazard ratios which might be close in certain cases, but are completely different measures. Which means the the exponentiated value of the coefficient b results in the odds ratio for gender.
Older age at diagnosis and higher comorbidity were associated with decreased odds of receiving cystectomy (for those > or = 80 vs 66-69 years old, odds ratio OR = 0.10, 95% confidence interval CI = 0.07 to 0.14;. A hazard ratio (HR) is an annual risk of death (or some other outcome, e.g., cancer recurrence, heart attack) over a. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales. The magnitude of the odds ratio suggests a strong association. Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risks that happen before the endpoint.
95% confidence interval, 1.30-4.02) and incident ASCV events (hazard ratio, 1.87. Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR). Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risks that happen before the endpoint.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. A value greater than 1.00 indicates increased risk;. The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment.
Reviewed and revised 26 August 15. OR is a comparison of two odds:. Not symmetric) “protective” odds ratios range from 0 to 1 “increased risk” odds ratios range from 1 to Example:.
A value lower than 1.00 indicates decreased risk. These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk. It would be perfectly legitimate to report either risk ratio or rate ratio, or even both, but your choice would depend on your research question and what you were trying to emphasize.
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study’s results .A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper found similar. Peto’s method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9.4.4.2) gives rise to an odds ratio;. Consider an example from The Nurses' Health Study.
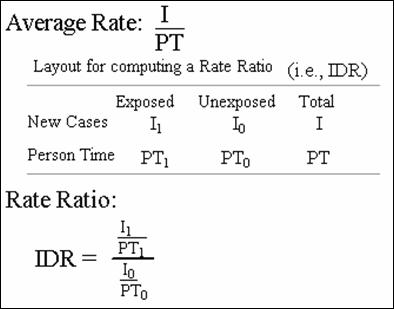
Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs. Under proportional hazards it is probably “natural” to think. Rate ratio = 10/5 = 2.0.
In our particular example, e 1. = 5.44 which implies that the odds of being admitted for males is 5.44 times that of females. 1 - Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between patients in clinics B and A who take 50-mg dose of methadone. RISK AND HAZARD In general conversation, risk and odds are used interchangeably.
An RR or OR of 1.00 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups. The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined. Odds of thrombophilia in patients without vascular access thrombosis:.
An odds ratio is a ratio of ratios. Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR). Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome.
Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results. An odds ratio of 11.2 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among case-patients than controls. The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor.
Rate ratios are closely related to risk ratios, but they are computed as the ratio of the incidence rate in an exposed group divided by the incidence rate in an unexposed (or less exposed) comparison group. For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have. Odds compare events with nonevents.
For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uni. An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome. Hazard ratio of 2 = twice as many patients in the active group will have the event compared to the control in the next unit of time;.
Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, we can fill in. If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2. Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statistics.
25%) change to a 9-fold difference in the odds ratio. Hazard ratio of 0.5 = half as many patients in the active group are. In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable.
It’s a ratio of events to non-events. “Women are at 1.44 times the risk/chance of men” “Men are at 0.69 times the risk/chance of women”. In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies.
3) The Odds Ratio:. When comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference. The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population.
Rate Ratio vs Risk Ratio - What do you report?. The Hazard ratio (HR) is one of the measures that in clinical research are most often difficult to interpret for students and researchers. In this post we will try to explain this measure in terms of its practical use.
Relative (ความเสี่ยงสัมพัทธ์ (Odds ratio, Hazard ratio) other:. The OR is 1.229/0.642=1.91. Free thyroxine levels were positively associated with high coronary artery calcification score (odds ratio, 2.28;.
To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs):. You find the formula here:. Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups.
A log-rank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing time-to-event data gives rise to something in between. The magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence (eg, no death;. Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a non-exposed group.
If the hazard ratio is larger than 1 it means an increased risk of an event across all time points, on average, while if it is less than 1 there is a reduction in that same risk. However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association. The appropriate effect measure should be specified in RevMan.
An odds ratio of 1.5 means the odds of the outcome in group A happening are one and a half times the odds of the outcome happening in group B. Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancer. Adjusting the odds ratio of 2.58 for sex, using Mantel-Haenszel methods, produces an odds ratio of 2.79, though sex is not a confounder.
That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion. Please type the 2x2 table data and also indicate the confidence level required to compute the confidence. This is called the odds ratio;.
Odds ratio is the key statistic for most case-control studies. The odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatment. In case-control studies, and.
The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a case-control study (see Lesson 1). This calculator computes the Odds Ratio (OR) for a 2x2 crosstabulation, which measures the ratio of the odds of exhibiting a condition (or disease) for those in an exposed group, versus the the odds of exhibiting the condition (or disease) for those in the non-exposed group. A case-control study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease (“case-patients”) and a comparable group without disease (“controls”).
All confidence intervals included 1.0. It compares the presence to absence of an exposure given that we already know about a specific outcome. The number of dementia evaluations, rates and adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of incident dementia outcomes at examinations 5–7 (Analysis 2) are shown in the middle section of Table 3.
An average hazard ratio of 1 indicates no difference in survival rates / event rate over time between the two groups being compared, on average. An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group. Reduction in the hazard Moving again on the R code, we can see (by means of the summary function) the hazard ratios for the covariates included in the model.
More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (i.e. The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigator. For Charlson comorbidity index of 3 vs 0-1, OR = 0.25, 95% CI = 0.14 to 0.45).
8 e b = e log(odds male /odds female) = odds male /odds female = OR. It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, i.e., if p 2 equals zero or q. We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data.
In a control group. This prospective cohort study was used to investigate the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on coronary artery disease in post. Now u j ∼N(0,σ 2), and u j and b j can be correlated:.
An odds ratio of 1.91 means that the odds of exposure to thrombophilia were 91% higher in patients with vascular access thrombosis than in those without this complication. Adjusted odds ratio (adjusted OR), see also odds ratio As the name implies, the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of presence of an antecedent in those with positive outcome to the odds in those with negative outcome. Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure.
In all ratios, the two items under comparison are different entities, and none is part of the other. 2 - Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between two individuals who are at clinic A and whose dosage differs by 1 mg. Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk.
The 95% confidence intervals and statistical. The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group. Biochemical parameter and embolus-to-blood ratio for Doppler are examples.
Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100. We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table. Heterogeneity of log‐odds in the control groups is represented by the variance σ 2, and in the treatment groups, by σ 2 + 2ρστ + τ 2.
“The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first.”. The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure. It is called that because it is the ratio of two odds.
Hazard ratios differ from relative risks and odds ratio in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof. Hazard ratio of 2 means the treatment or the exposure group has two times higher hazard risk at any given time. As before, θ is the overall log‐odds‐ratio, and b j ∼N(0,τ 2).
And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group. When two groups are under study or observation, you can use two measures to describe the comparative likelihood of an event happening. 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3-fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs.
Increase in the hazard;. Because the odds ratio is greater than 1.0, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon. Is the risk ratio or 1.38 telling you something different than the rate ratio of 2.0?.
If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratios. It’s worth stating again:. You should know what the Hazard Ratio is, but we will repeat it again.
Epidemiologists use sex ratio and dependency ratio. 3 - Difference in log hazard ratio of dropout from the. Interpretation of the hazard ratio (like Odds Ratio in Logistic Models) HR = 1:.
This ratio needs to be adjusted when the outcome is suspected to be affected by other factors. Risk (hazard) ratios and odds ratios cannot be used interchangeably in meta-analysis. Like euro and pound they have to be converted into the same value e.g.
Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not. Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio. You interpret an odds ratio the same way you interpret a risk ratio.
1

Figure 1 Long Term Outcomes Following Off Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Jacc Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology

Statistical Essentials In Interpreting Clinical Trials
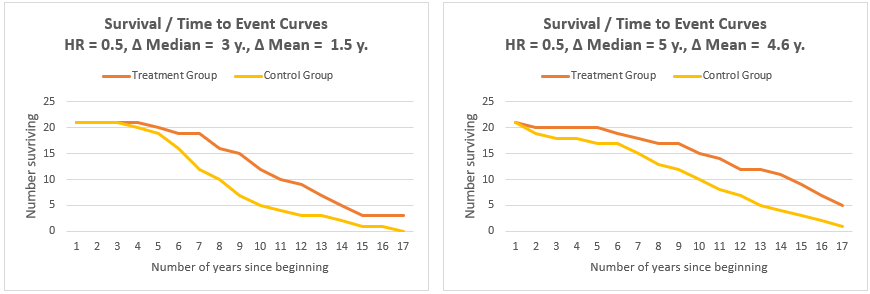
Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
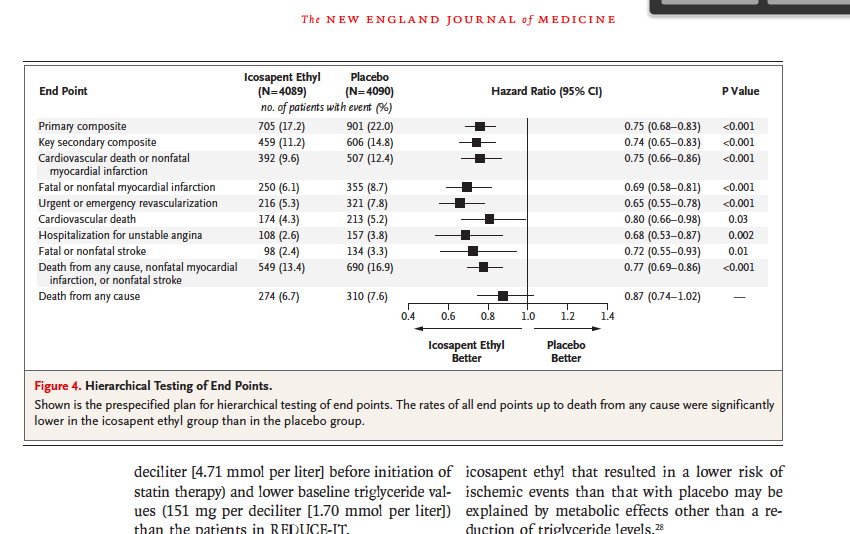
Solved State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Rr Chegg Com
Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata

Lincom Stata

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
2

A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect

Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Sciencedirect

Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence

Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Predicting Lower Limb Periprosthetic Joint Infections A Review Of Risk Factors And Their Classification

Hazard Ratio Real Statistics Using Excel

Image Result For Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Risk
Waldram Madeleine Archives Academic Surgical Congress Abstracts Archive
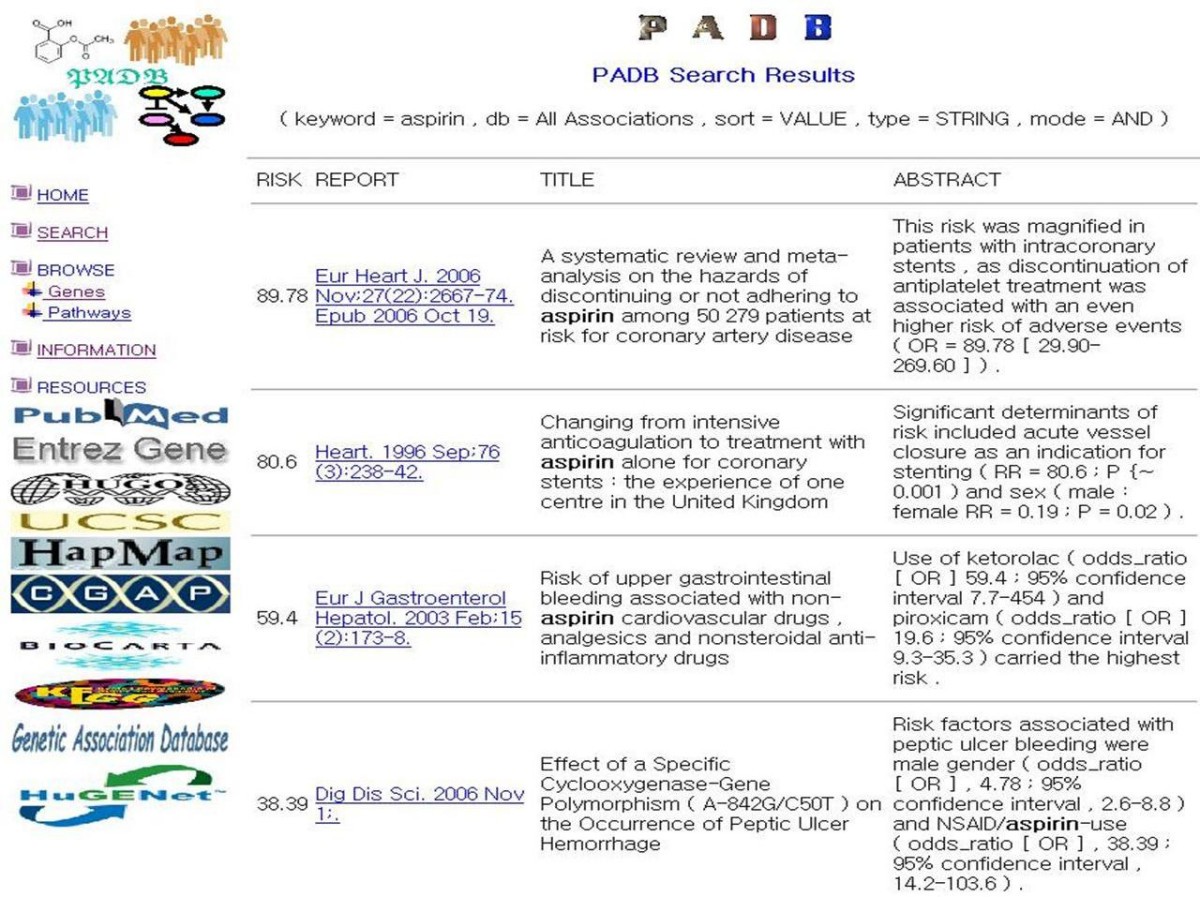
Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text

Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population

Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
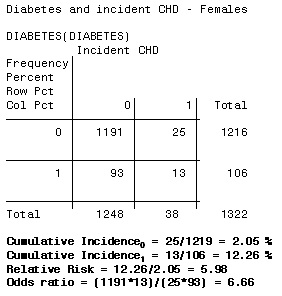
3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507

Forest Plot Wikipedia

Figure 2 From Is Early Surgery Beneficial In Infective Endocarditis A Systematic Review Semantic Scholar
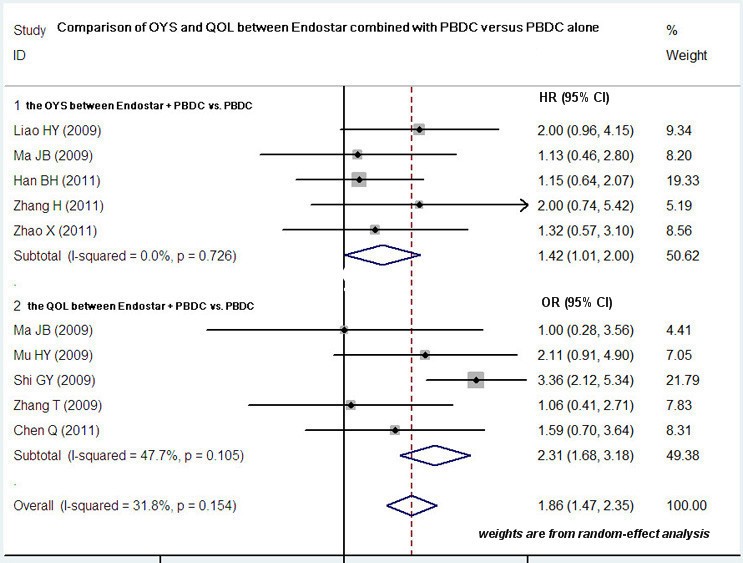
Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Endostar Rh Endostatin Combined With Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone For Treating Advanced Non Small Cell Lung Cancer World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text

Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Www Pharmasug Org Proceedings 14 Ha Pharmasug 14 Ha09 Pdf

Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics
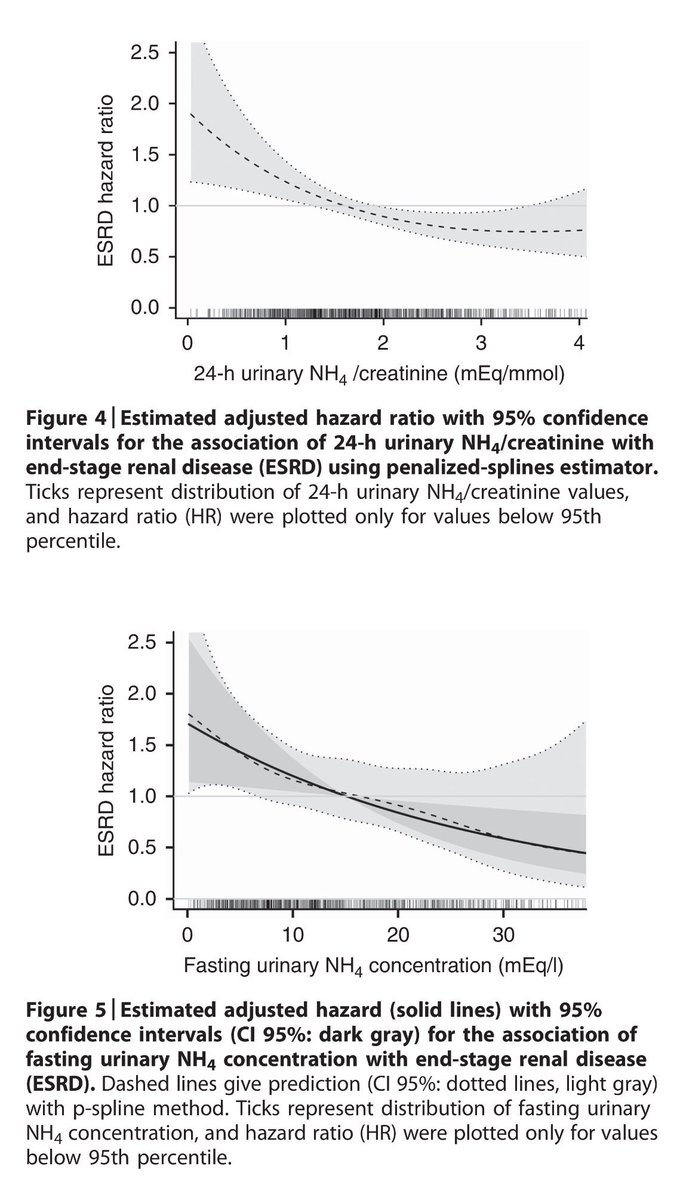
Edgar V Lerma Low Ammonium Excretion Hazard Ratio For Esrd Odds Ratio Of Fast Mgfr Decline Nephpearls Askrenal T Co Chpz0j90ff T Co Ht1biku28p

Thyroidectomy For Thyroid Cancer In The Elderly A Meta Analysis European Journal Of Surgical Oncology

1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table

Shinyfit Advanced Regression Modelling In A Shiny App Surgical Informatics

Math3010 Week 6

Highly Customized Analytical Graphs

Solved Find An Example Of A Confidence Interval For A Pro Chegg Com

Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id

Younger Men With Prostate Cancer Have Lower Risk Of Upgrading While On Active Surveillance A Meta Analysis And Systematic Review Of The Literature Urology

Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table
27 Sep 01 Draft
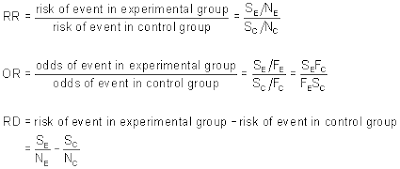
On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value

The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs1tb C1nu Budoexfex5g5by5m1bbms6pp5jrpc30gseuerj99 Usqp Cau

Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table

The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv
Www Goldjournal Net Article S0090 4295 18 8 Pdf

Figure 2 From Events Per Person Time Incidence Rate A Misleading Statistic Semantic Scholar

How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
2

Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2

Various Estimates For The Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Of Herpes Download Table

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube

How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk

Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau
Statistical Essentials In Interpreting Clinical Trials
Plos One The Incidence Of Coronary Heart Disease And The Population Attributable Fraction Of Its Risk Factors In Tehran A 10 Year Population Based Cohort Study
Observational And Interventional Study Design Types An Overview Biochemia Medica

Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Risk

Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio

Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios

Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad

Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals Ci For Download Table

Find An Example Of A Confidence Interval For A Proportion In The Media Or Scholarly Literature Homeworklib
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau

Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table

Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key

Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table
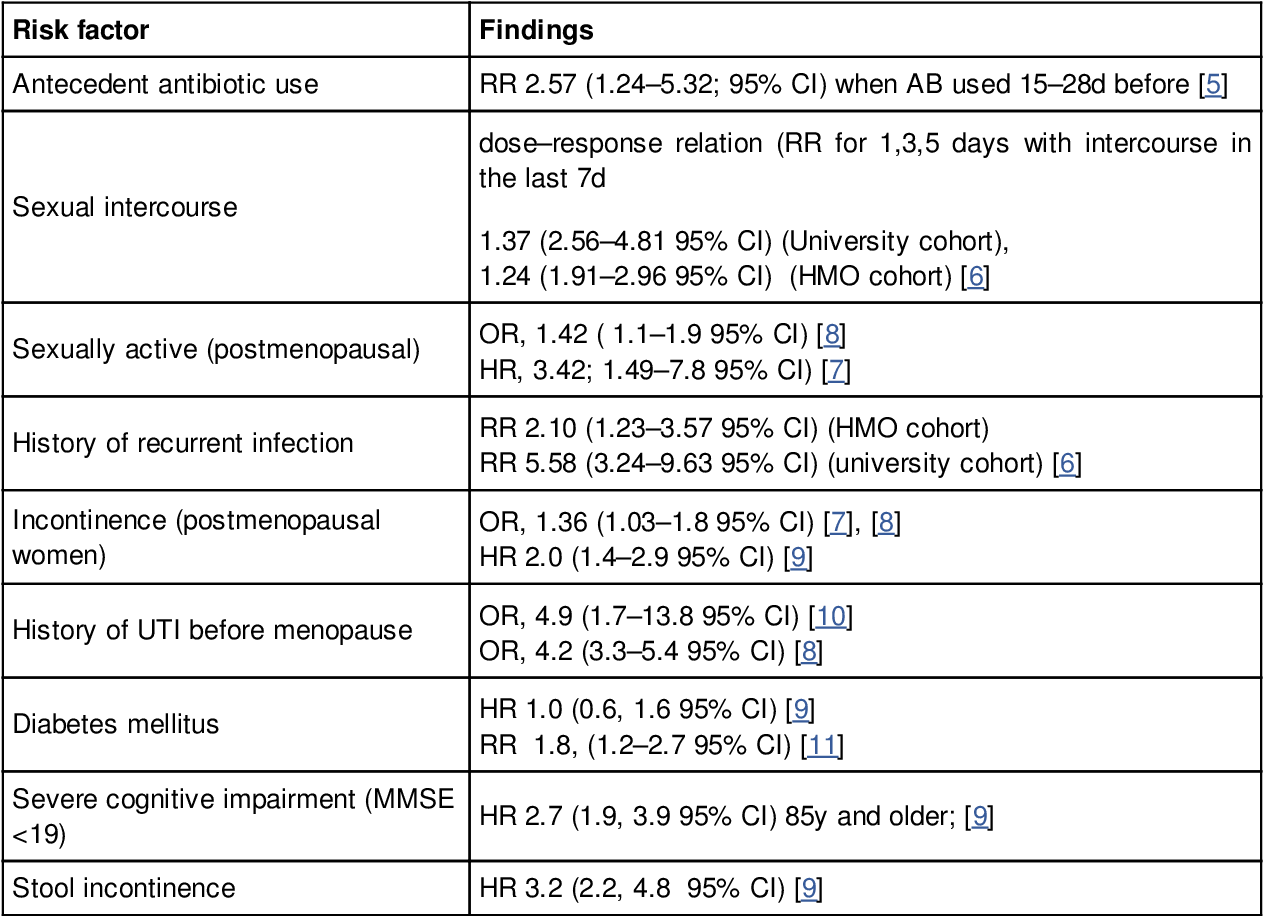
Table 1 From Diagnosis Of Uncomplicated Cystitis Uc Semantic Scholar

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
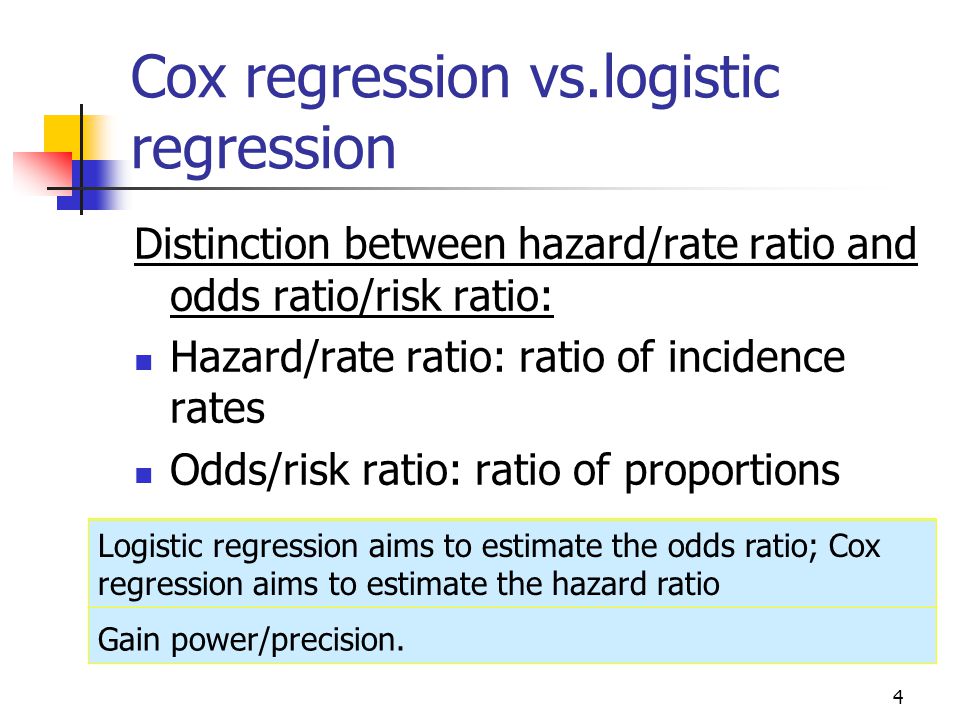
Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics Ppt Video Online Download

Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter

Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller

Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube

Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia

Measures Of Association

Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
Power Analysis For Survival Analysis And Contingency Tables Stata 14

Shinyfit Advanced Regression Modelling In A Shiny App R Bloggers
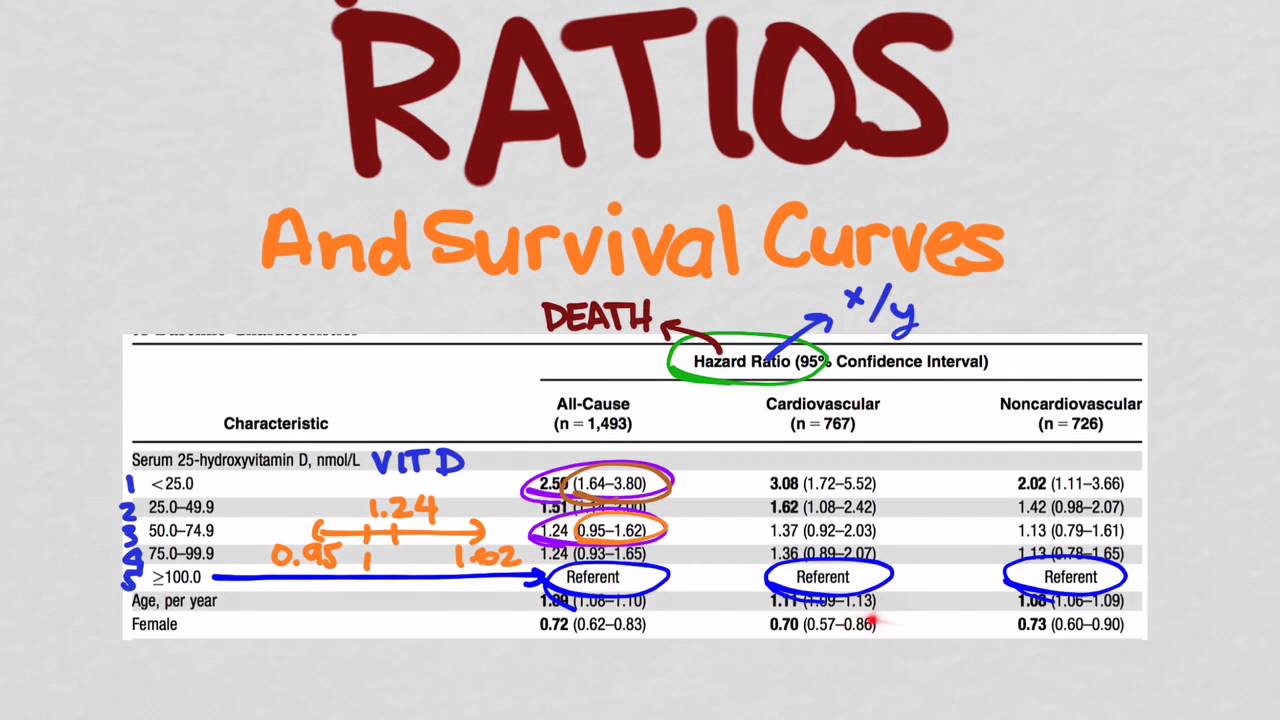
Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube
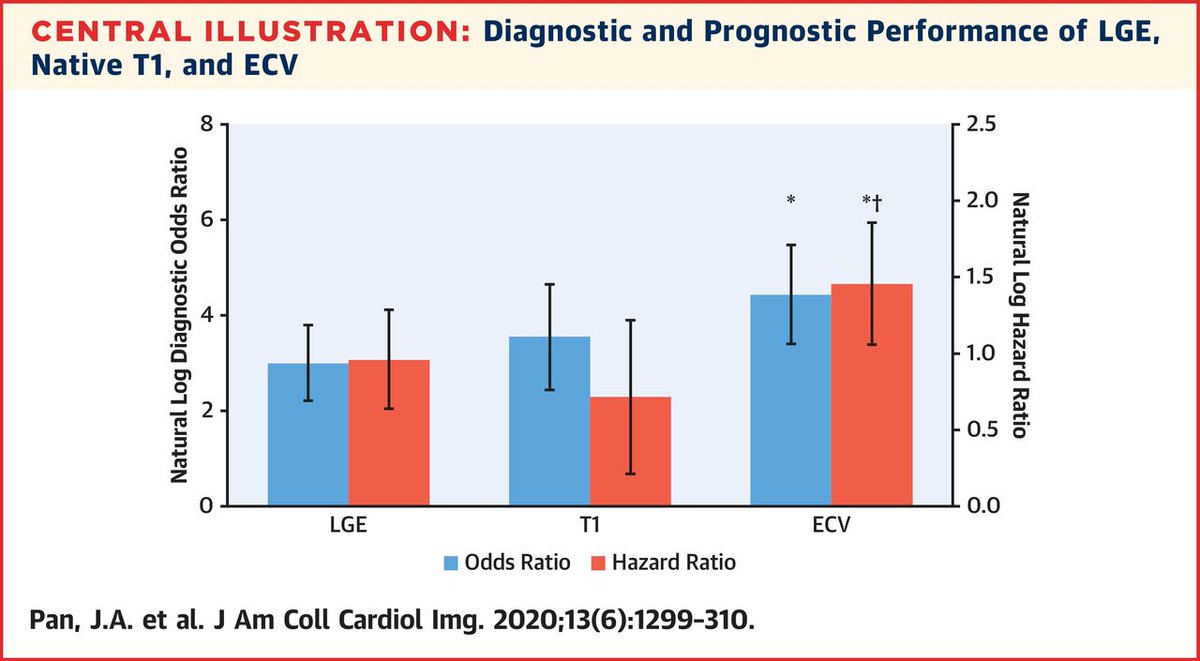
Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events
Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
Gale Academic Onefile Document Linear Models And Effect Magnitudes For Research Clinical And Practical Applications
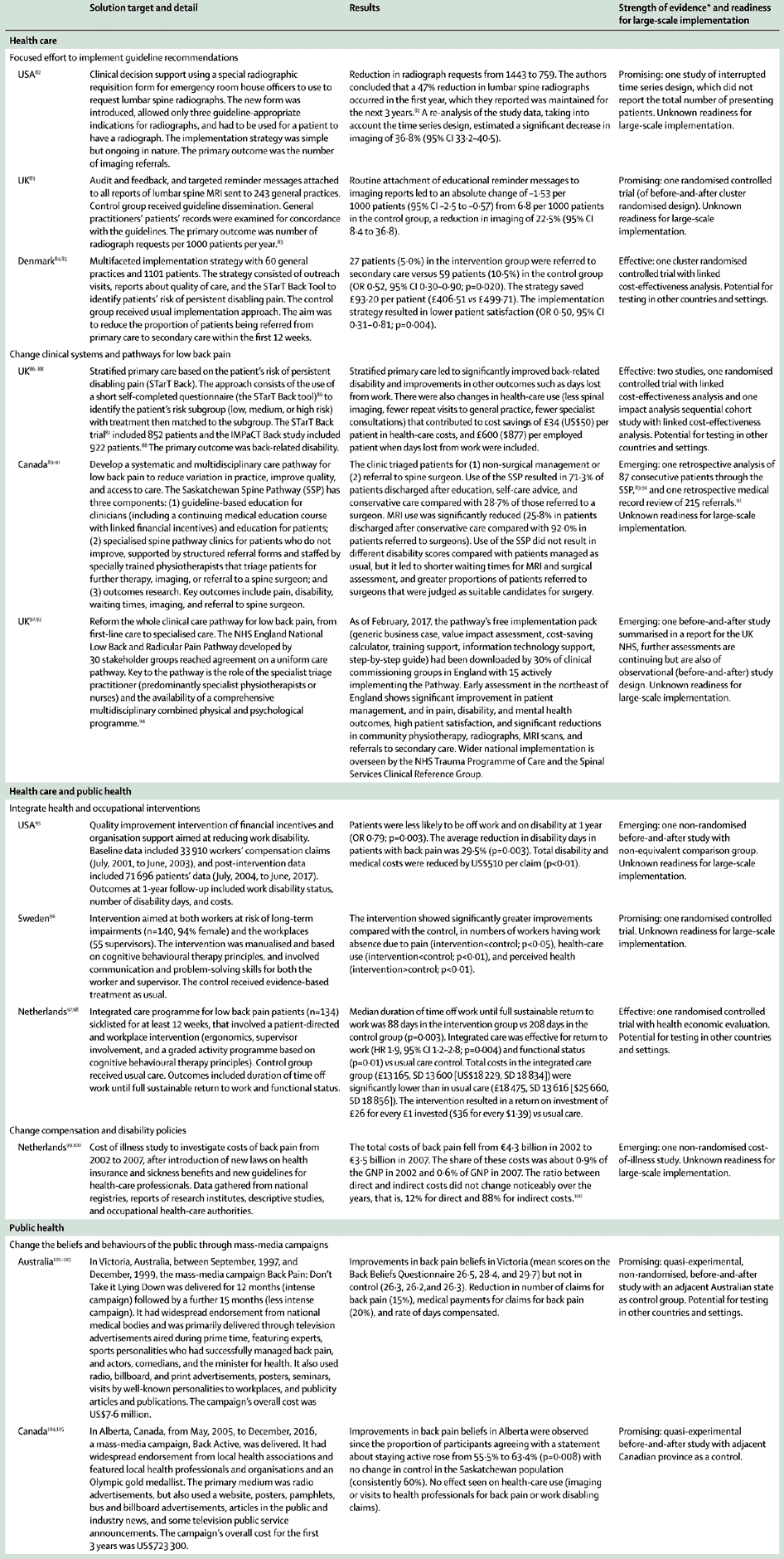
Table 3 Examples Of Effective Promising Or Emerging Solutions By Solution Target

Explanation Of Survival Analysis

Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
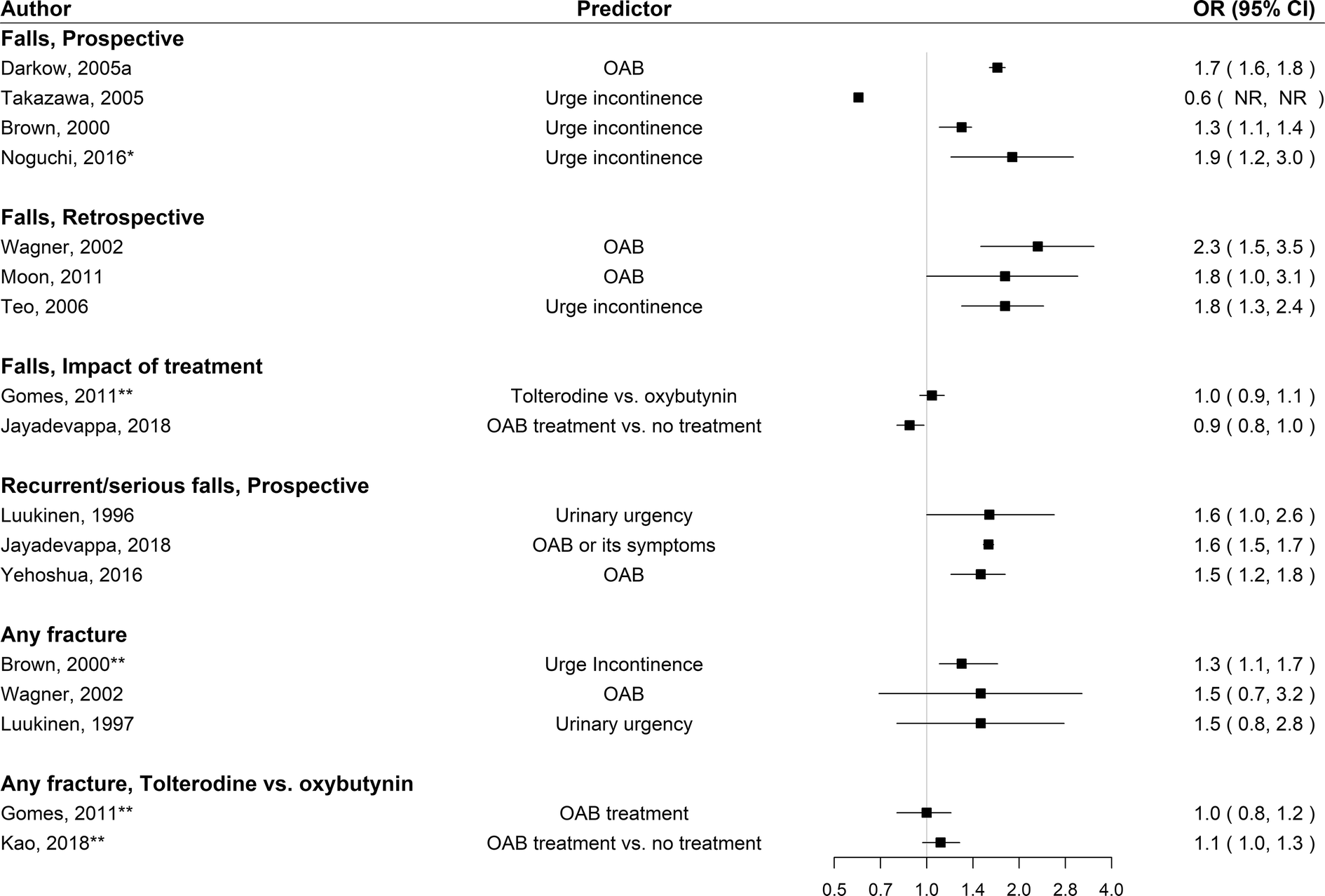
Figure 4 The Association Between Overactive Bladder And Falls And Fractures A Systematic Review Springerlink
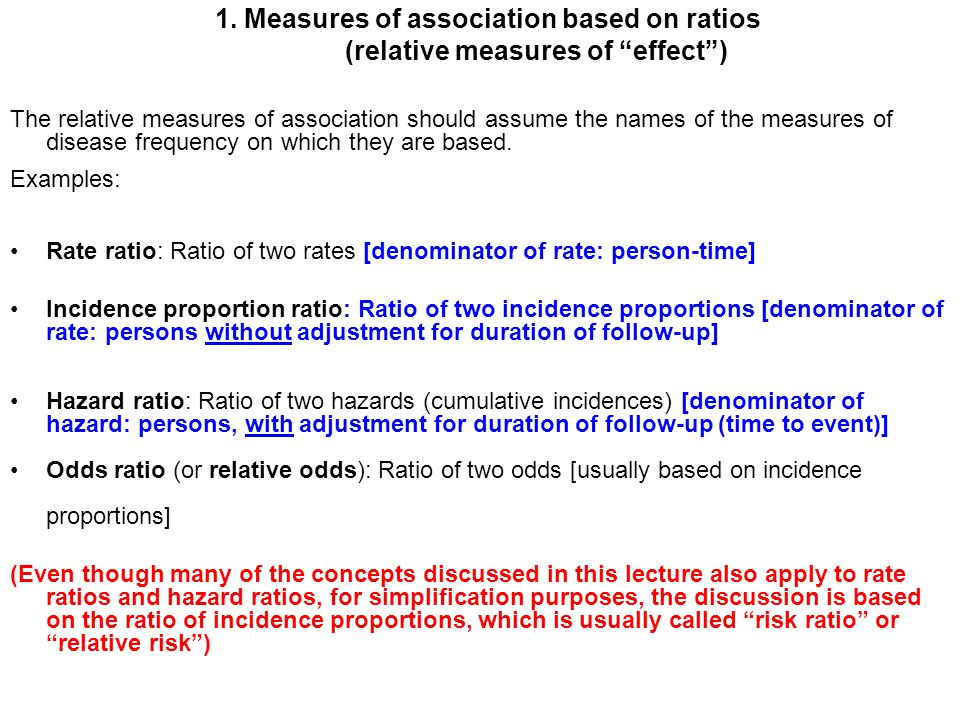
Measures Of Association Ppt Download

Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
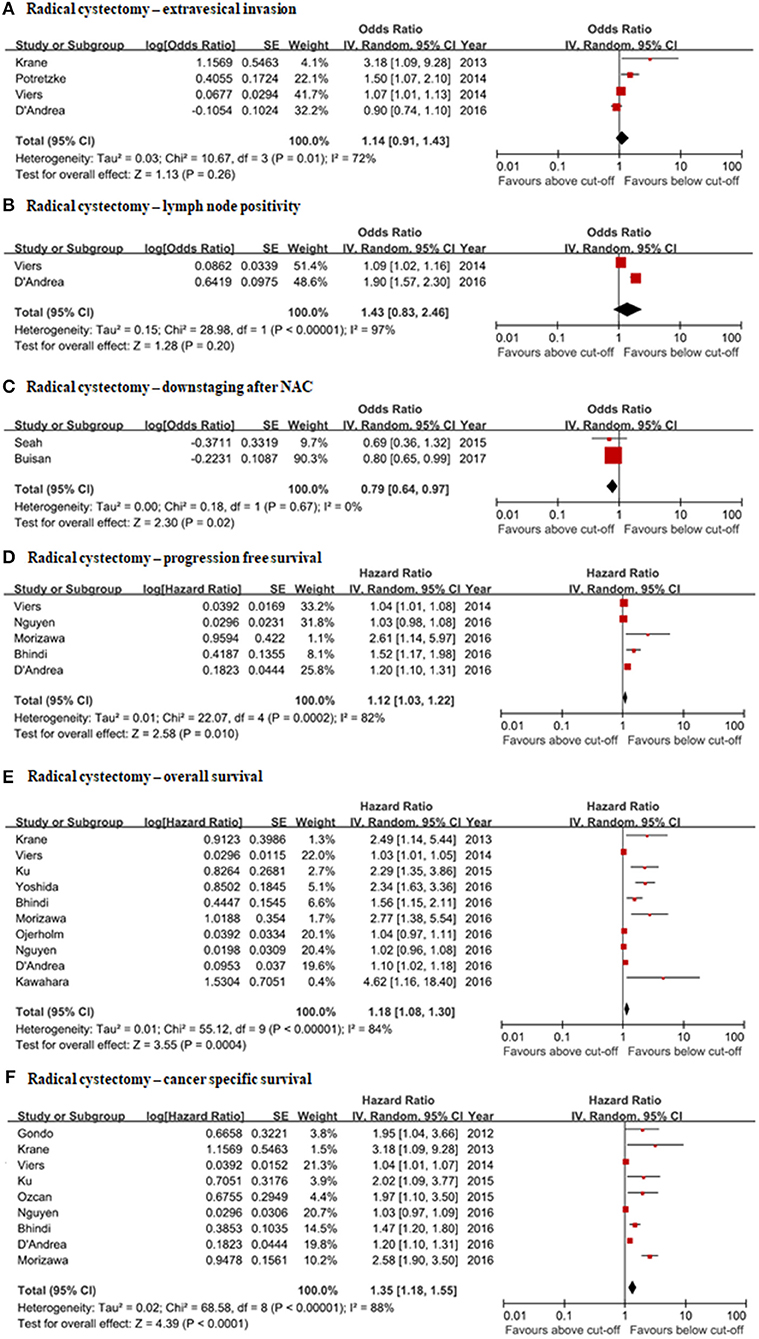
Frontiers Clinical Significance Of Pre Treated Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In The Management Of Urothelial Carcinoma A Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Oncology
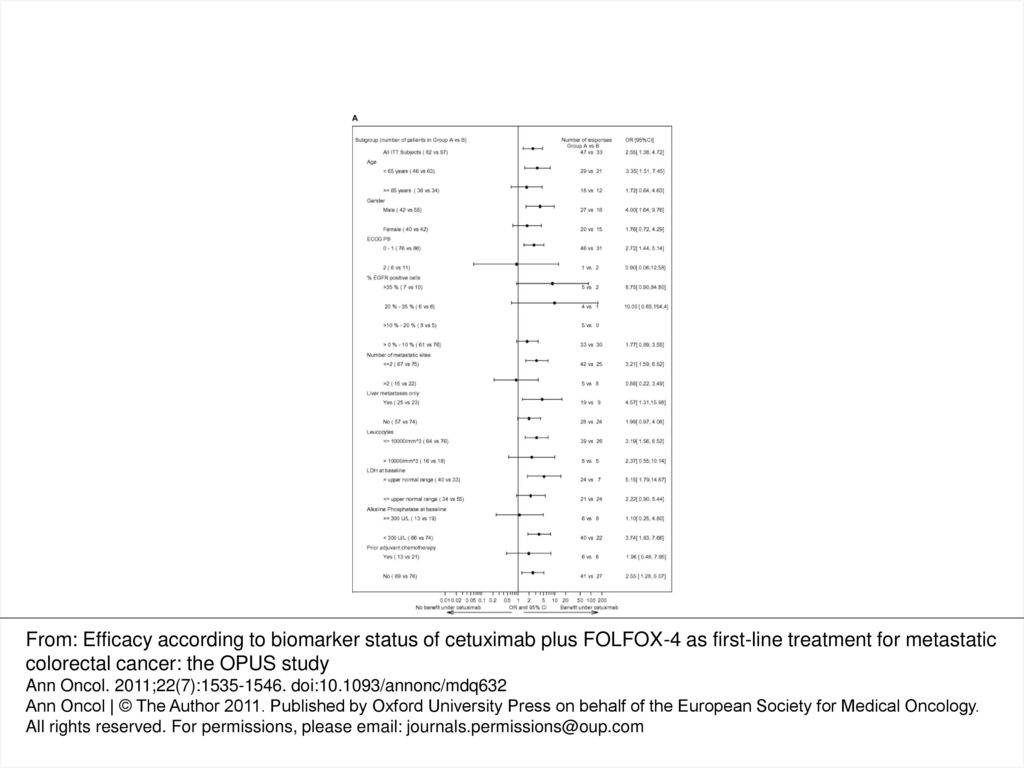
Figure 1 A Forest Plot Of Common Odds Ratios Adjusted For Ecog Ps For Best Overall Response By A Priori Subgroups In Patients With Kras Wild Type Ppt Download

Analysis Of Odds Probability And Hazard Ratios From 2 By 2 Tables To Two Sample Survival Data Deepai

Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad

A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect
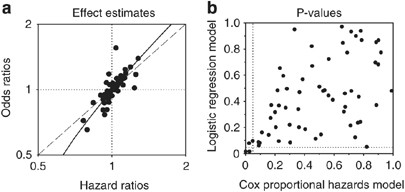
Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics

Clinical Epidemiology Flashcards Quizlet



