Odds Vs Risk Ratio
Pdf Fallacy Of Using Odds Ratio As A Measure Of Association In Prospective Studies

Relative Risk Odds Ratio

Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research

How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy

Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough

Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
A probability will be a familiar concept to readers of this blog.

Odds vs risk ratio. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions. It is the risk of a.
You know the difference between risk and odds. A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group. Probability is the likelihood of an event in relation to all possible events.
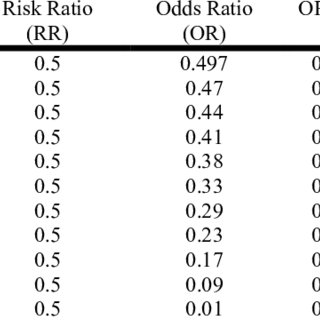
Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among non-smokers (the same, but with non. More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (i.e. In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio.
Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results. 25%) change to a 9-fold difference in the odds ratio. The outcome generated is called lenses, to indicate if the hypothetical study participants require corrective lenses by the time they are 30 years old.
3) The Odds Ratio:. Odds ratio vs risk ratio. An RR or OR of 1.00 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups.
In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the. The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 9.2.a). Risk difference is an absolute measure of effect and it is calculated by subtracting the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals from that of unexposed.
Before we look at odds and risk ratios, let’s be clear on what odds and probabilities are (this couple of paragraphs added on August 18). In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for case-control studies, as the relative risk cannot be estimated. Literature Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research.
A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects. Rather the odds is threefold greater. If the Odds ratio is 0.7 then it indicates a protective effect - I.e a reduced odds of exposure in case vs control group.
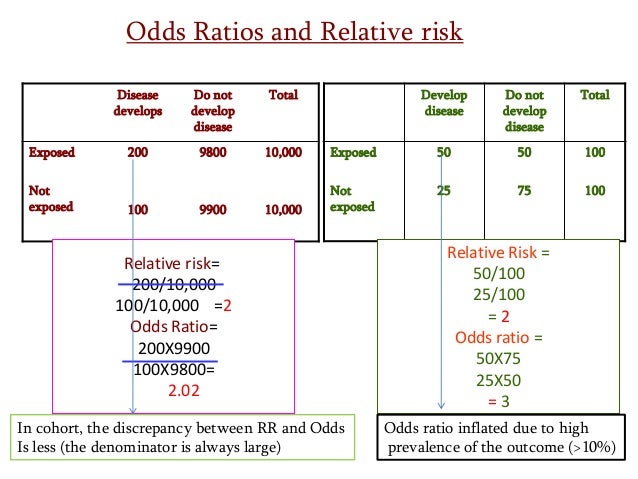
Because the incidence rate in the non-delirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the study. Relative risk is a ratio of probabilities. Odds ratio (100 × 7,9) ⁄ (1,900 × 80) = 5.2 Notice that the odds ratio of 5.2 is close to the risk ratio of 5.0.
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio. The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population. In fact, the odds ratio has much more common use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk.
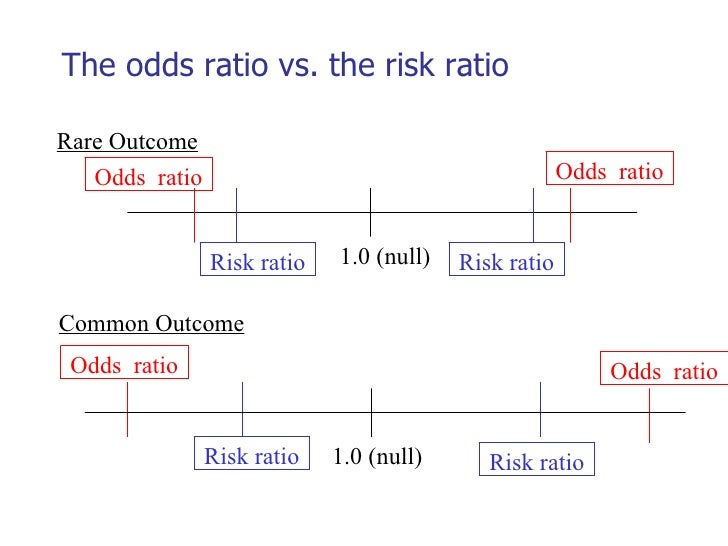
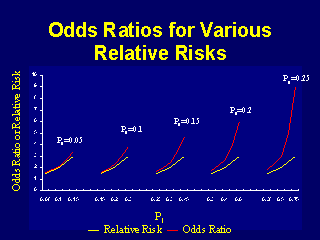
To measure an association with exposure, the use of prevalence ratios (PR) or odds ratios (OR) are possible. Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not. That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio.
Odds ratio is the key statistic for most case-control studies. In a control group. Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome.
Just as with RR, where the ratio of two risks was taken for two separate groups, a ratio of two odds can be taken for two separate groups to produce an odds ratio (OR). When the event of interest is rare (i.e. For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uni.
In essence, we regard. Let’s say that one quarter of tigers are diseased. If the risk of the events is high, then the OR and the RR cannot be used interchangeably, since they tend to be quite different because the risk is bounded by the values of 0 and 1, whereas the odds can have values from 0.
However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio. The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second. A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold.
Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a non-exposed group. Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature. Thus in situations with rare outcomes an odds ratio can be interpreted as if it were a risk ratio, since they will be numerically similar.
Therefore, odds ratios are generally interpreted as if they were risk ratios. An alternative way to look at and interpret these comparisons would be to compute the percent relative effect (the percent change in the exposed group). A value lower than 1.00 indicates decreased risk.
Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancer. No, that’s the interpretation of a risk ratio!. In meta-analysis for relative risk and odds ratio, studies where a=c=0 or b=d=0 are excluded from the analysis (Higgins & Green, 11).
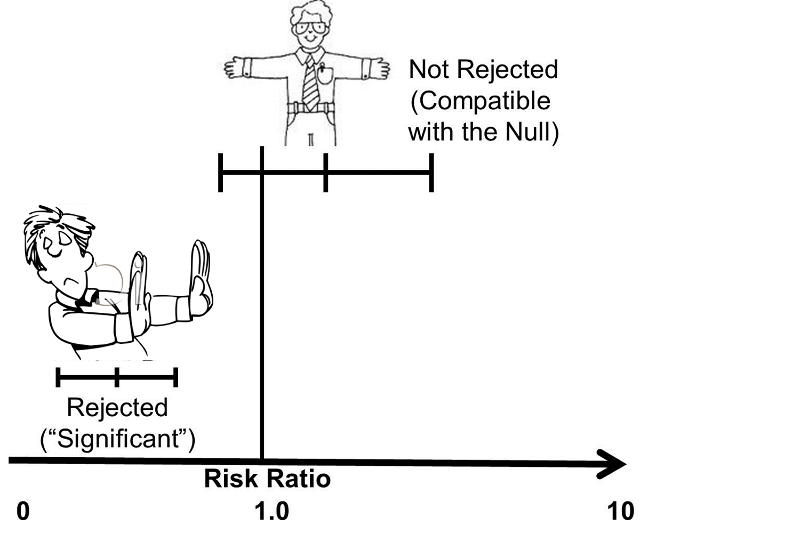
Otherwise it is a risk ratio, which is not the same calculation. The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise. A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group.
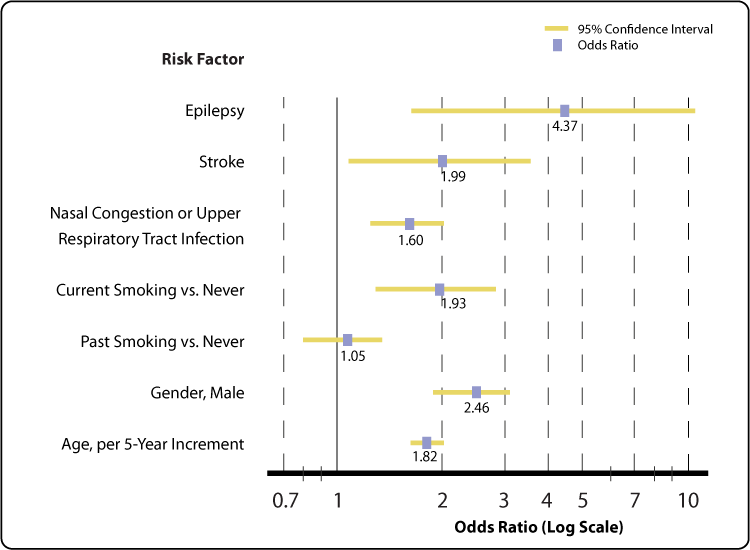
Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not. 16 We also consider the log link, which corresponds to the log‐risk‐ratio. In one study on the familial occurrence of dystocia, the authors stated, “The risk is increased by more than -fold (odds ratio 24.0, 95% confidence interval 1.5 to 794.5) if one sister had dystocia…” The baseline risk was 11% and the actual RR was 6.75.
But an OR of 3 doesn’t mean the risk is threefold;. So no evidence that drinking wine can either. Note also that, while this result is considered statistically significant, the confidence interval is very broad, because the sample size is small.
Instead of reporting how many times the risk one group bears relative to the other, it reports how many times the odds one group bears to the other. To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs):. In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies.
For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have. Difference Between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk 1. Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type.
The correct interpretation of an odds ratio is:. 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3-fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs. The resulting mixed‐effects logistic regression, with log‐odds‐ratio as the effect measure, belongs to the class of GLMMs, discussed in meta‐analysis by Turner et al 15 and Stijnen et al.
Risk Ratio is often expressed as a factor and a whole positive number, such as “… is times more likely…” The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the. In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable. The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it’s that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
Odds ratio versus relative risk. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987).
The odds of having the disease in the exposed group are higher than the unexposed. For the odds ratio to be a good approximation, the cases and controls must be representative of the general. Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR).
Hazard ratio deals with a two part ( level ) explanatory variable and is an instantaneous risk over the course of the study. A value greater than 1.00 indicates increased risk;. In human epidemiology, much has been discussed about the use of ….
A hypothetical data set was created to illustrate two methods of estimating relative risks using Stata. The RR is much simpler to interpret and is most likely consistent with everyone’s intuition. The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group.
However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association. That reduced risk is 1-odds so will be 30 percent reduced risk fo exposure. After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 1.4 (mortality is 1.4 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium).
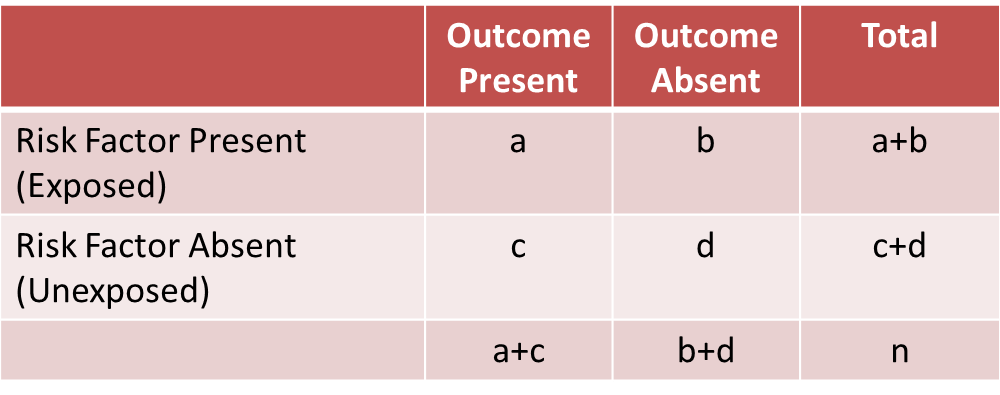
The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor. One of the most commonly observational study designs employed in veterinary is the cross-sectional study with binary outcomes. When the risk ratio cannot be obtained directly (such as in a case-control study), the odds ratio is calculated and often interpreted as if it were the risk ratio.
OR is a bit more complicated and uses the formula A/ (1-A)/ B/ (1-B). Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk. Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups.
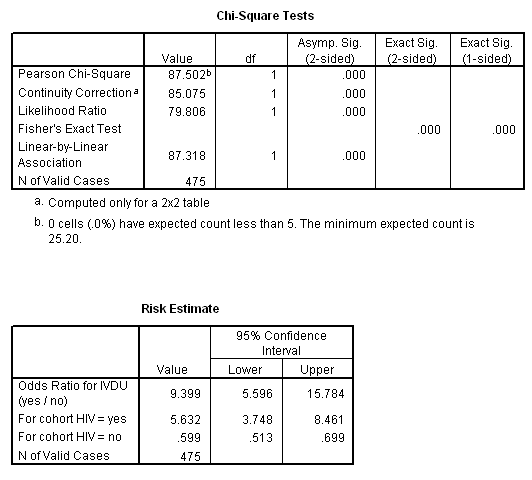
A RR of 0.5 means the risk is cut in half. OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 3:76 0:37 = 10:16:. The magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence (eg, no death;.
The 95% confidence intervals and statistical. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. The risk ratio, the incidence rate ratio, and the odds ratio are relative measures of effect.
Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (<10%). Statistical significance is linked to the p-value or CI- which we cannot infer from only the odds ratio. The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to non-occurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole.
If a horse wins 2 out of every 5 races, its probability of winning is 2/5 (40%). You must be clear that it is the oddsof dying that are being compared. Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimal.
Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, we can fill in. These are all part of Survival Analysis a statistical method used in clinical trials. (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio).
In a study on men given a new stati. From which we can infer that if the risk or the probability of failure is low ( P <0.1), then the OR is a good approximation of the RR, and they can be used interchangeably. In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size.
Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 0.1), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (0.1 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 0.2). The odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options:. The probability of it occurring is low), the odds and risk ratios are numerically quite similar.
Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio. Start studying Risks Ratio, Odds Ratio. “Women are at 1.44 times the risk/chance of men” “Men are at 0.69 times the risk/chance of women”.
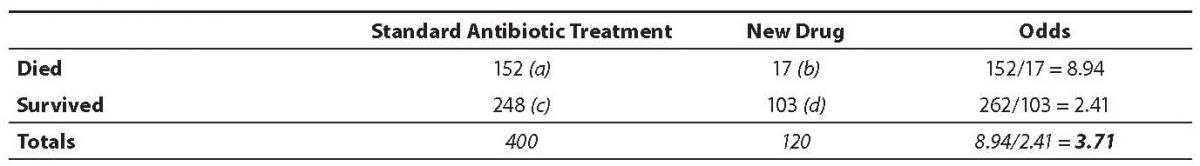
If we pick a tiger at random, there is a 1/4 (or 0.25) probability that we pick a. Not symmetric) “protective” odds ratios range from 0 to 1 “increased risk” odds ratios range from 1 to Example:. The patients who received standard care had an oddsof dying 3.71 times more than patients treated with the new drug.
"The odds ratio is very similar to the risk ratio, particularly if a disease is rare.

Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube

Biostatistics Series Module 8 Assessing Risk Hazra A Gogtay N Indian J Dermatol
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsg4su2mr8na0fhj Fifitqg198udx Emcfjr4lbf73sjgn9d K Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnh1uw23gmkmgfg0omhxyeez8cwvljdyhd6xi8w J Un51itbu Usqp Cau
The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica
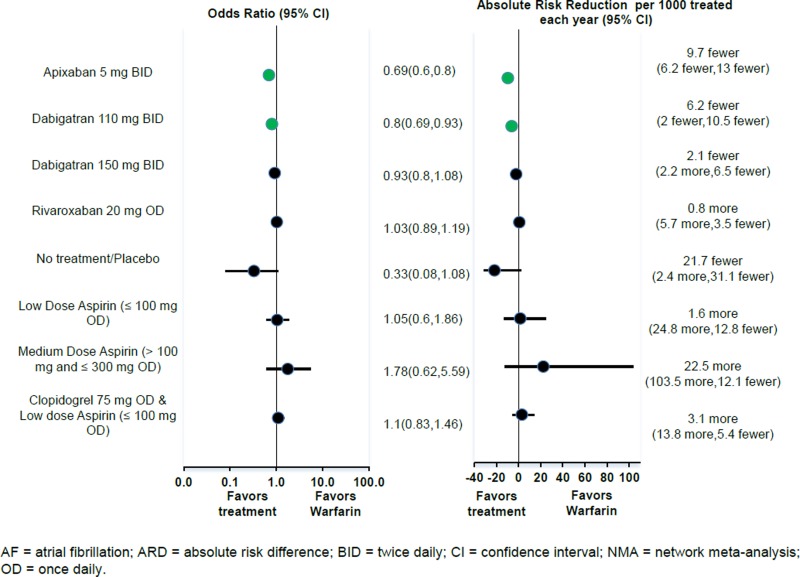
Figure 3 Odds Ratio And Absolute Risk Difference Of Major Bleeding For Antithrombotic Therapies Relative To Adjusted Dose Warfarin For Patients With Af Fixed Effects Nma Antithrombotic Agents For The Prevention Of Stroke
Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Approximates The Risk Ratio When The Disease Is Rare And Other Conditions Are M Course Hero
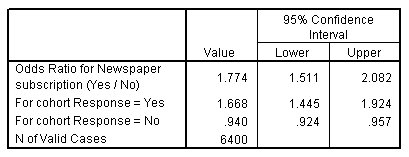
Ibm Knowledge Center
A Stratified Analysis

Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
Excel Odds Ratio Foodborne Disease Outbreak Toolkit

Glossary Of Research Terminology

Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube

Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube

Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube

Math3010 Week 6

Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases

Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube

Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Q Tbn 3aand9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
Marg Innovera
Selected Risk Factors For Smell Impairment Nidcd

Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study Cohort Study Case Study Study

Math3010 Week 6

A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc

Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To

Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study

Lecture3

Forest Plot Wikipedia
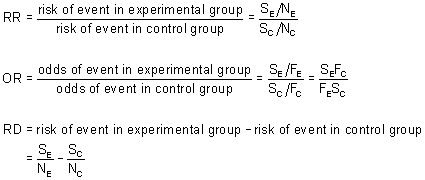
Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd

Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine

Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk

Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table
54

Risk Difference Rd Risk Ratio Rr And Odds Ratio Or For The Download Table
Estimating Risk
Lecture3
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq5tpzikqe8jiy9iqzxyqcbaqndofe8d2iabvvrkarpadvgvm8o Usqp Cau

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect

Related Image Cohort Study Cross Sectional Study Case Study

Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube

Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios For Hospital Mortality Download Scientific Diagram

Ppt Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute Risk Differences And Risk Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk

Forest Plot Showing Study Specific And Pooled Odds Ratio Or Diamond Download Scientific Diagram

Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
Confidence Intervals And P Values

What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download

Pdf Understanding Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Related Terms As Simple As It Can Get Semantic Scholar

Risks In Biomedical Science Absolute Relative And Other Measures Kim J Bang H Dent Hypotheses

Relative Risk Wikipedia
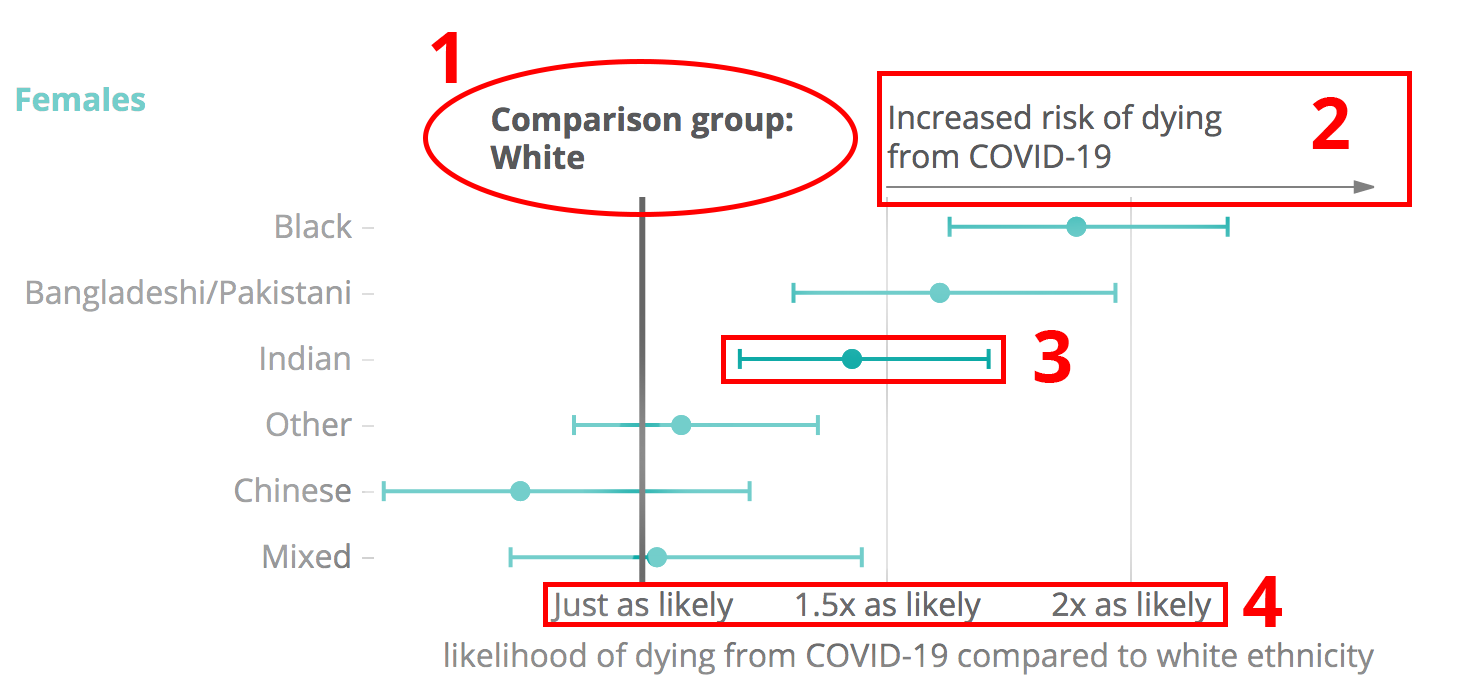
Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau

The Risks Of Odds Ratios Gallis 19 Bjog An International Journal Of Obstetrics Amp Gynaecology Wiley Online Library

Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
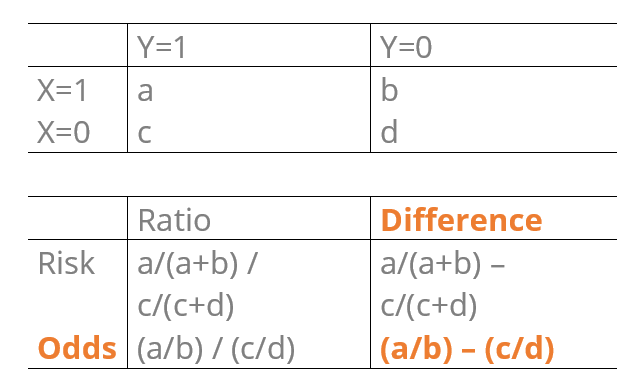
Tim Morris Hate Odds Ratios Hate Risk Ratios Hate Risk Differences Well I M Feeling Cantakerous This Morning And Have Your Back Introducing The Odds Difference Unless You Just Hate Everything

Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout
Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True

Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Abstract Europe Pmc

Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To

Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj

Odds Ratio Relative Risk
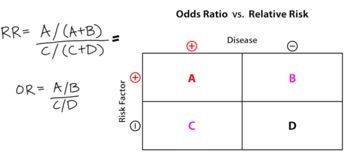
Behavioral Flashcards Memorang

Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated

Relative Measures Of Association For Binary Outcomes Challenges And Recommendations For The Global Health Researcher
44

Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club

The Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Comparing Download Scientific Diagram

Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Orthodontics Clinic

Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor

Assessment Of Multiplicative Interaction Using Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram

Literature Search

Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo

Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training

Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk

Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things

Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood

Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
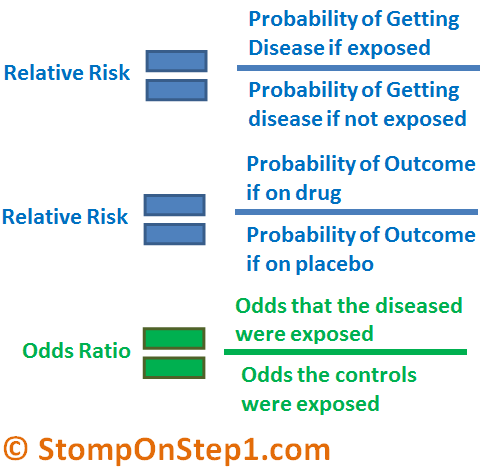
Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
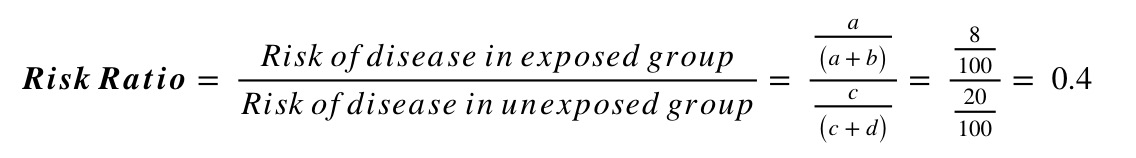
Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge

Students 4 Best Evidencea Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence

Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
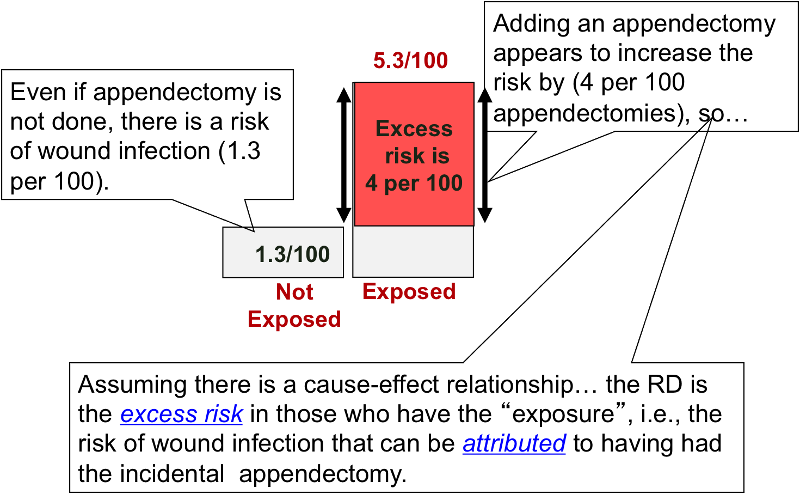
Risk Differences And Rate Differences

Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals

Image Result For Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Risk

Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
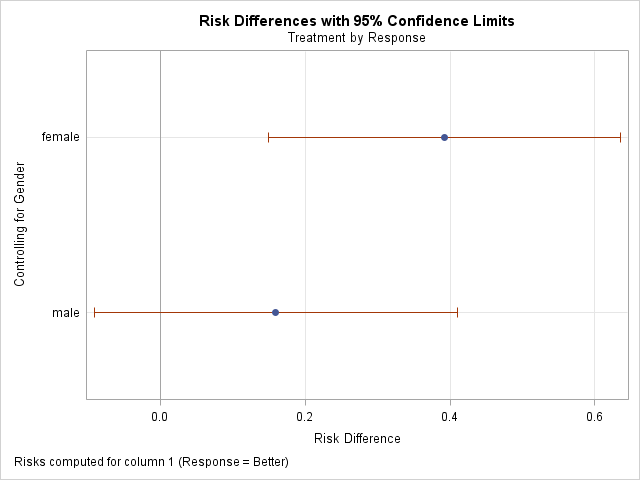
Risk Differences Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Plots With Proc Freq

Research Statistics Basics

Comparison Of Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Based On Download Table

Figure 3 From Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar



